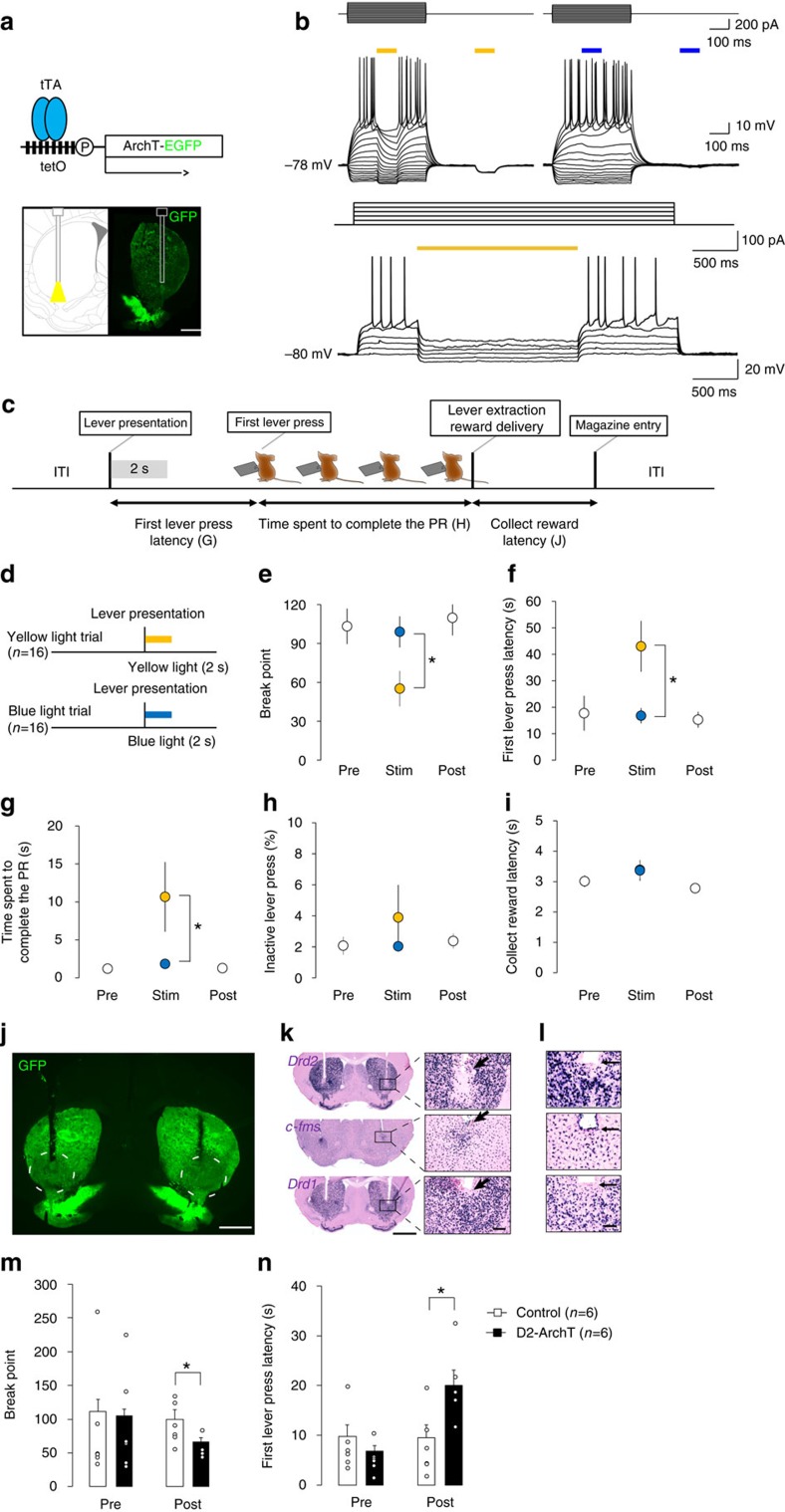
Figure 6. Optogenetics-mediated inhibition/ablation of VLS D2-MSNs induces reductions in goal-directed behaviour.
(a) Drd2-tTA-dependent ArchT expression (upper) and illumination of bilateral VLS D2-MSNs (lower). Scale =1 mm. (b) ArchT-expressing MSN response to current injection and illumination during whole cell voltage recording. Yellow, but not blue, light illumination suppressed action potential generation (upper panel). Two seconds-yellow light illumination suppressed action potential generation without inducing rebound excitation (lower panel). (c) Timing of illumination in the PR task. Yellow or blue light was applied immediately after every lever presentation for 2 s (grey shade). ITI: inter-trial interval. (d) The experimental schedule of optogenetic inhibition (eight D2-ArchT bigenic mice were used and 16 sessions were conducted). (e–i) The effects of acute optogenetic inhibition of VLS D2-MSN on behavioural parameters in the PR task. The yellow-light illumination decreased break point (e) and prolonged first lever press latency (f) and time spent to complete the PR (g). These behavioural changes were restored to the pre-baseline levels on the following day. Yellow-light illumination did not change the collect reward latency (h) or %inactive lever press (i). (j–l) Continuous 3-h illumination induced a cell type-specific ablation in the VLS. GFP florescence was attenuated in the VLS (j) Scale, 1 mm. In the D2-ArchT bigenic mice (k), Drd2 mRNA labelling disappeared (upper) and c-fms-positive microglia were activated (centre) while Drd1 mRNA expression did not change (lower) in the area below the tip of the optic fibre (arrow). Scale, 50 μm. In the monogenic controls (l), no apparent changes were observed in Drd2 (upper), c-fms (centre), or Drd1 (lower) mRNA expressions. Scale,50 μm. (m,n) The effects of optogenetic ablation of VLS D2-MSNs on behavioural parameters in the PR task (n=6 for each group). The continuous 3-h yellow-light illumination decreased break point (m) and prolonged first lever press latency (n). *P<0.05, Paired t-test compared with the monogenic control.