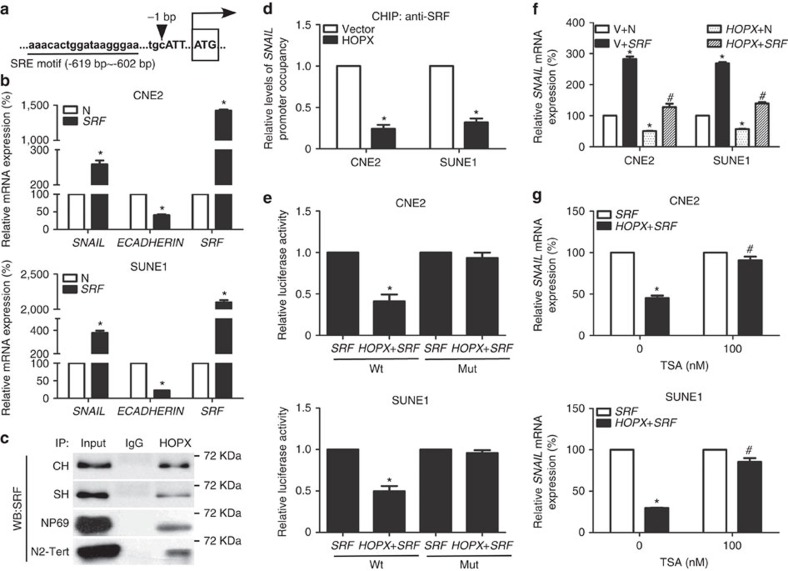
Figure 6. HOPX epigenetically inhibits SRF-mediated SNAIL transcription in NPC.
(a) Sketch map of the SRE motif within the SNAIL promoter predicted by JASPAR software. Upper case letters: exon. (b) Relative SNAIL, ECADHERIN and SRF mRNA expression levels were determined via real-time RT–PCR in CNE2 and SUNE1 cells stably overexpressed the control N or SRF. Mean±s.d.; *P<0.01 compared with N; Student's t-tests. (c) Co-IP assays were used to measure the interaction between HOPX and SRF in CH, SH, NP69 and N2-Tert cells. CH and SH cells indicated CNE2 and SUNE1 cells with stable HOPX overexpression; WB, western blotting assay. (d) ChIP real-time PCR assays were applied to measure the enrichment of SRF in the SNAIL promoter in CNE2 and SUNE1 cells stably overexpressed the vector or HOPX. Mean±s.d.; *P<0.01 compared with vector; Student's t-tests. (e) Wild-type and mutant SNAIL-luciferase reporters were constructed and co-transfected with SRF or/and HOPX in CNE2 and SUNE1 cells. Luciferase reporter assay was used to detect the luciferase activity of SNAIL promoter. Mean±s.d.; *P<0.01 compared with SRF; Student's t-tests. (f) CNE2 and SUNE1 cells were co-transfected with HOPX or/and SRF. V and N were used as empty vectors of HOPX and SRF, respectively. Relative SNAIL mRNA expression was measured via real-time RT–PCR. Mean±s.d.; *P<0.01 compared with V+N; #P<0.01 compared with HOPX+N; Student's t-tests. (g) Real-time RT–PCR was applied to assess the relative SNAIL mRNA expression following transfection with SRF or/and HOPX. TSA (0 and 100 nM) was treated with CNE2 and SUNE1 cells. Mean±s.d.; *P<0.01 compared with SRF; #P<0.01 compared with TSA (0 nM); Student's t-tests. These data are representative of three independent experiments.