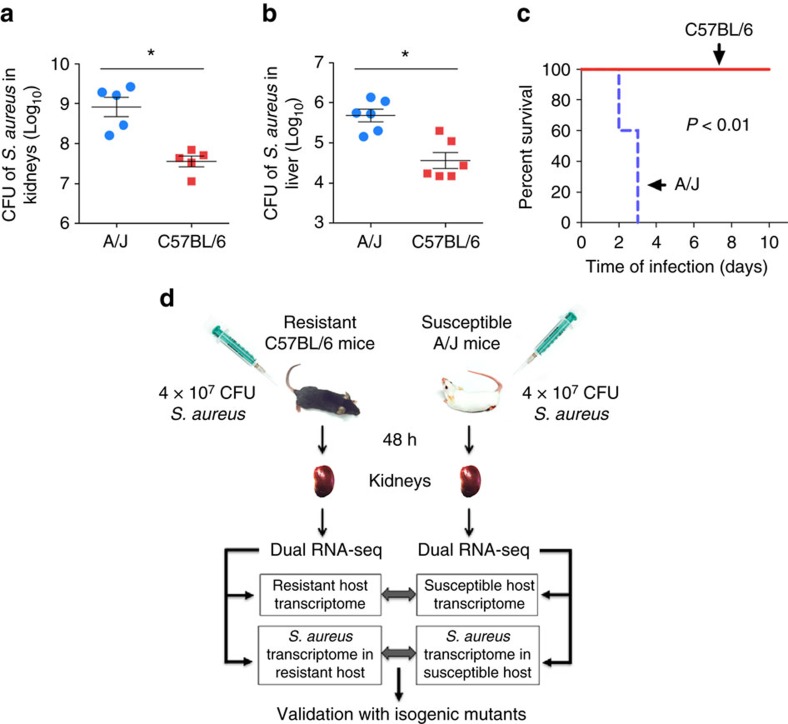
Figure 1. A/J and C57BL/6 mice exhibit opposed levels of resistance to S. aureus.
Bacterial loads in the kidneys (a) and liver (b) of A/J and C57BL/6 mice at 48 h after intravenous inoculation with 4 × 107 CFU of S. aureus SH1000. Each symbol represents the bacterial counts determined in an individual mouse and the horizontal lines represent the average±s.d. for each mouse strain. One representative experiment out of three independent experiments is shown (n=6, t-test, *P<0.05). (c) Survival curves of A/J and C57BL/6 mice intravenously infected with 4 × 107 CFU of S. aureus SH1000 (n=5, log-rank test, P<0.01). (d) Schematic summary of the experimental design for dual RNA-seq analysis. Susceptible A/J mice and resistant C57BL/6 mice were infected intravenously with 4 × 107 CFU of S. aureus SH1000, their kidneys removed at 48 h after bacterial inoculation and subjected to dual RNA-seq analysis to simultaneously determine the gene expression profile of the host and pathogen in the same sample. The genes differentially expressed by S. aureus in A/J and C57BL/6 mice were identified and related to the infection-associated transcriptional response of the corresponding mouse strain. The effect of targeting a virulence factor differentially expressed by S. aureus SH1000 between infection of A/J and C57BL/6 mice was also determined.