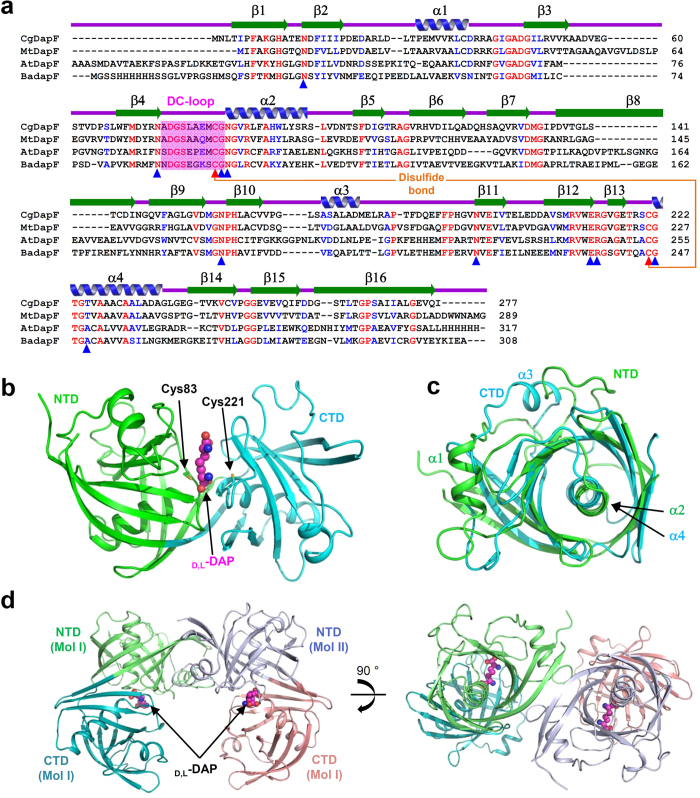
Figure 1. Overall structure of CgDapF.
(a) Amino acid sequence alignment of the DapF proteins. Identical and highly conserved residues are presented in red and blue colored characters, respectively. Secondary structure elements are shown and labeled based on the structure of CgDapF. The DC-loop is shown in a magenta-colored box. Two catalytic cysteine residues, Cys83 and Cys221, involved in the disulfide bond formation are distinguished with orange-colored line and marked with red colored triangles. Residues involved in the substrate binding are marked with blue colored triangles. Cg, Mt, At, and Ba represent DapF from Corynebaterium glutamicum, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Arabidopsis thaliana, and Bacillus anthracis, respectively. (b) Monomeric structure of CgDapF. A monomeric CgDapF is shown as a cartoon diagram. NTD and CTD are distinguished with green and cyan colors, respectively. d,l-DAP molecule bound in the enzyme is shown as a sphere model with a magenta color. (c) Superimposition of structures of NTD and CTD. The NTD and CTD structure are presented with a color scheme in (b). (d) Dimeric structure of CgDapF. The dimeric structure of CgDapF is presented as a cartoon diagram with one monomer with a color scheme in (b) and the other in light-blue and salmon for the NTD and CTD, respectively. The bound d,l-DAP is shown as a sphere model with a magenta color. The right-side figure is a 90° rotation in the vertical direction from the left-side figure.