Figure 1.
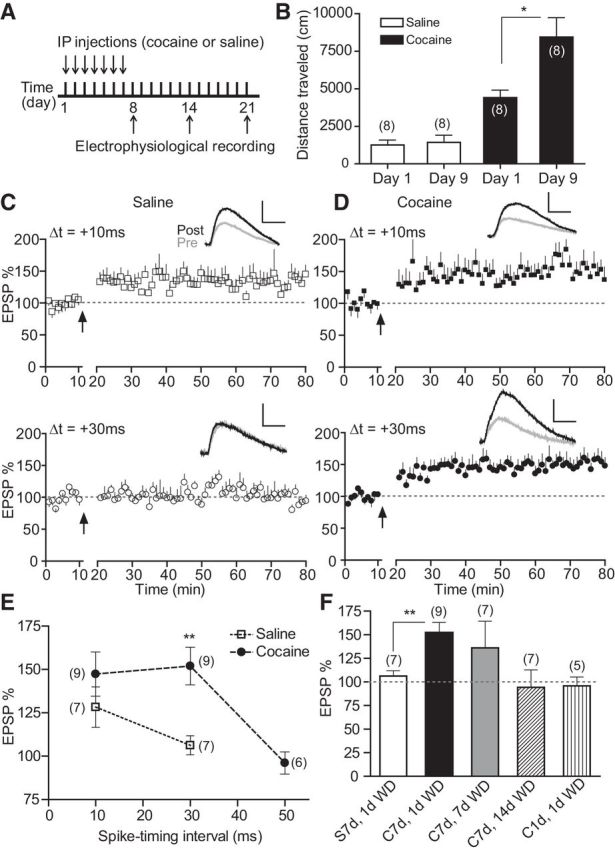
Repeat, but not single, cocaine exposure extends t-LTP timing window during an early period of withdrawal. A, Schematic of repeated cocaine or saline injection protocol. B, Cocaine-induced locomotor sensitization. Total distance traveled during a 30 min period after saline or cocaine challenge on day 1 and day 9 was measured. C, t-LTP induction by 60 EPSP–AP pairs at Δt = +10 ms, but not +30 ms, in slices from saline-treated mice. D, t-LTP induction by 60 EPSP–AP pairs at both +10 ms and +30 ms in slices from repeated cocaine-treated mice. E, Summary of t-LTP induction at different Δt's in repeated saline and cocaine conditions. F, Summary of t-LTP induction at +30 ms under different treatment and withdrawal conditions. S, Saline; C, cocaine; WD, withdrawal. Insets, Representative EPSPs 5 min before and 30 min after t-LTP induction. Scale bars, 2 mV, 20 ms. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, unpaired two-tailed t tests. Arrows indicate the start of t-LTP induction. Values in parentheses indicate number of cells recorded from at least three mice in each group.
