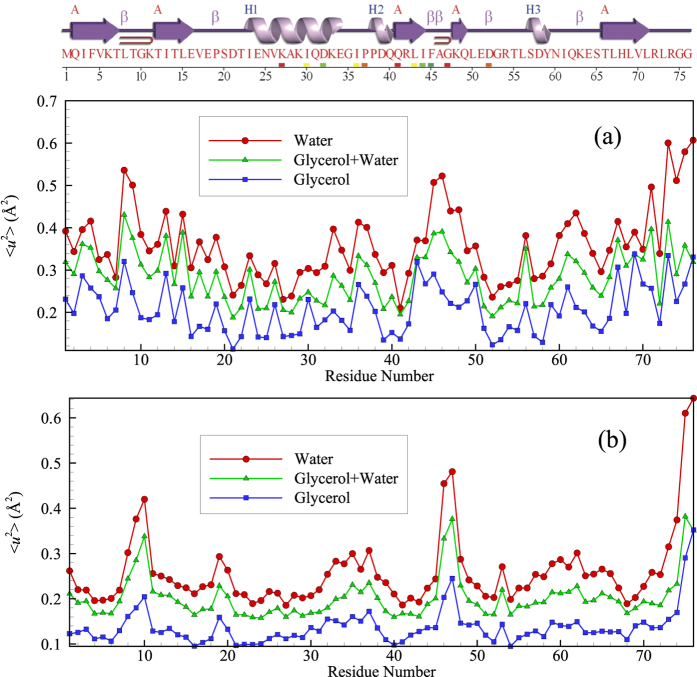
Figure 5.
(a) Variation of average 〈u2〉 values of all carbon atoms per residue along the sequence of ubiquitin. (b) Variation of 〈u2〉 along the sequence of the Cα atoms of ubiquitin. Top figure exhibits ubiquitin’s secondary structure. The present simulations qualitatively accord with experimental estimates of the Cα atoms 〈u2〉 for ubiquitin as a function of residue number50. We show both the alpha carbon and all the carbon atoms of the protein because we find that a description of the collective atomic motion within the protein requires that all of the carbon atoms to be considered rather than just those of the protein backbone. Many experimental and computational studies focus on just the alpha carbons.