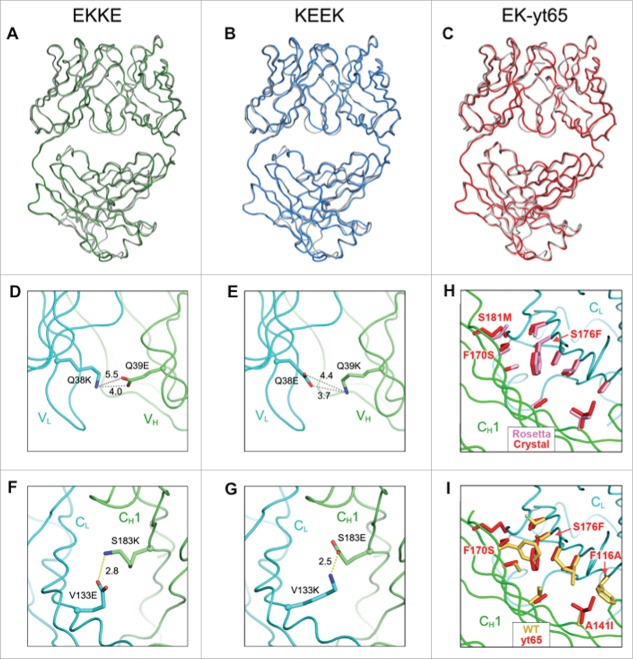
Figure 4.
X-ray crystallographic analysis of engineered anti-HER2 Fab fragments (Table S2). (A-C) Crystal structures of engineered variants demonstrating close superposition with the parent anti-HER2 Fab (PDB 1FVE,34 gray). (A) Fab structure of EKKE variant (PDB 5TDN, green) containing the mutations, VH Q39E, CH1 S183K, VLQ38K and CL V133E. (B) Fab structure of KEEK variant (PDB 5TDO, blue) containing the mutations, VH Q39K, CH1 S183E, VLQ38E and CL V133K. (C) Fab structure of EK-yt65 (PDB 5TDP, red) containing the mutations, VH Q39E, CH1 yt65H, VLQ38K and CL yt65L. (D-G) X-ray crystallographic analysis of engineered anti-HER2 Fab fragments highlighting the engineered charge pairs. (D) VH Q39E interactions with VL Q38K in the EKKE variant. (E) VH Q39K interactions with VL Q38E in the KEEK variant. (F) CH1 S183K interactions with CL V133E in the EKKE variant. (G) CH1 S183E interactions with CL V133K in the KEEK variant. (H, I) X-ray crystallographic structure of the CH1/CL interface highlighting the yt65 mutations. (H) The side chains of the mutated residues in the crystal structure of yt65 (red) were superimposed with the structure modeled with Rosetta (pink). (I) The side chains of the mutated residues in the crystal structure of yt65 (red) were superimposed on the corresponding positions in the parent structure (yellow).