Figure 5.
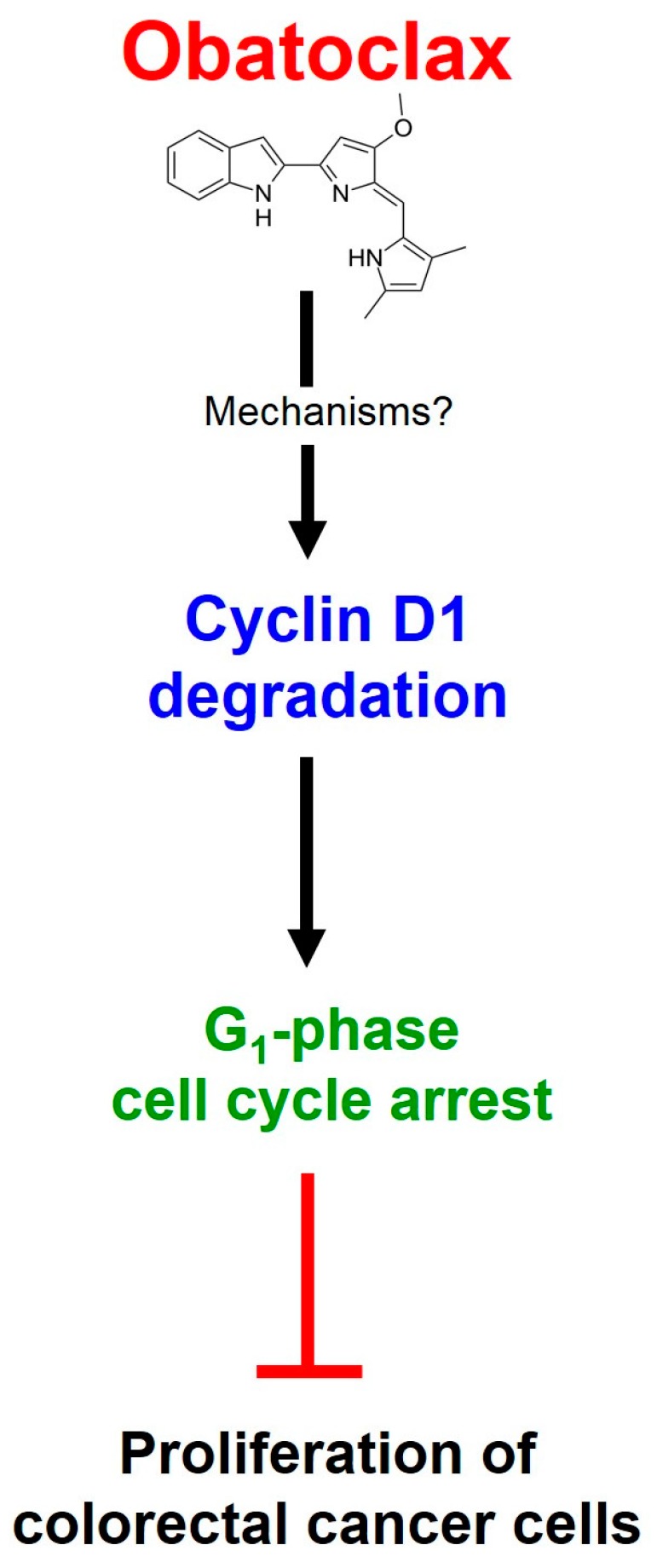
Schematic model depicting the mechanisms of action underlying obatoclax-induced antiproliferation. Obatoclax targets cyclin D1 for proteasome-mediated degradation to downregulate cyclin D1, leading to delayed G1-phase cell cycle progression, and the consequent inhibition of cell proliferation in a panel of human colorectal cancer cell lines.
