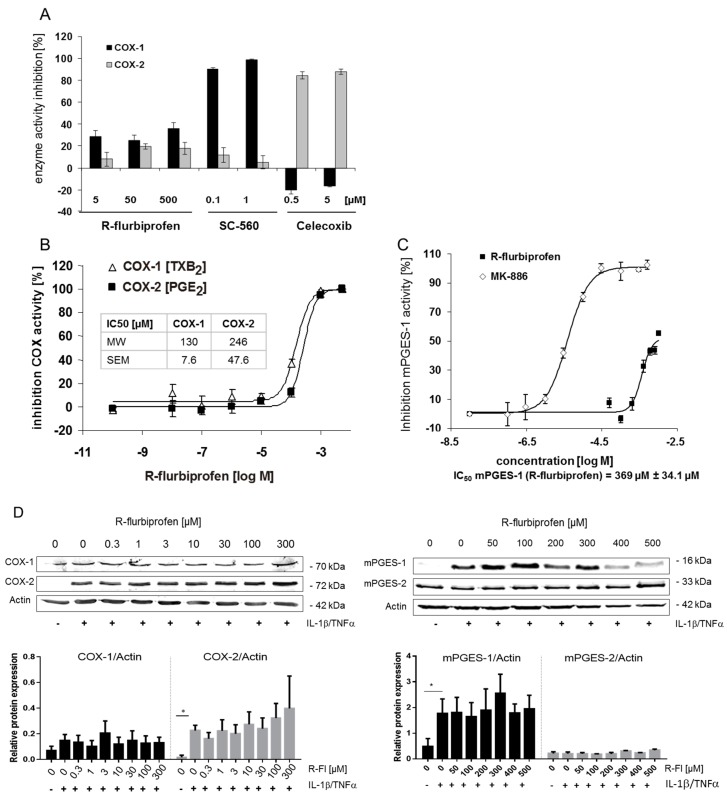
Figure 2.
(A) COX inhibitor screening assay: in vitro inhibition of purified COX-1 and COX-2 protein by R-flurbiprofen, SC-560, and celecoxib. R-flurbiprofen inhibited COX-1 and COX-2 activity only marginally, without concentration dependency. Means ± S.E.M. of four independent experiments; (B) Human whole-blood assay in vitro: human blood was pre-incubated with R-flurbiprofen or vehicle (DMSO) and subsequently stimulated either with Ca2+-ionophore (20 μM A23187) for induction of COX-1 activity, resulting in the formation of thromboxane B2 (TXB2), or with LPS (5 mg/mL) for induction of COX-2 activity, resulting in the formation of PGE2. IC50 values were calculated using a sigmoid Emax model. Data presented are means ± S.E.M. of four independent experiments; (C) mPGES-1 activity assay: mPGES-1 activity was measured in the microsomal fraction of HeLa cells in vitro. R-flurbiprofen only marginally affected mPGES-1 activity, with an IC50 of about 370 µM. In contrast, MK-886 inhibited mPGES-1 activity with an IC50 of 4 µM. IC50 values were calculated using a sigmoid Emax model. Data presented are means ± S.E.M. of four independent experiments; (D) Western blot analysis of COX-1 and COX-2 (whole cell lysate) and mPGES-1/2 (microsomal fraction). One representative experiment out of three is shown, as well as the quantification of three Western blots. Data presented are means ± S.E.M. of three independent experiments; statistical analysis was done with one-way ANOVA. Significant p values are shown as: * p ≤ 0.05.