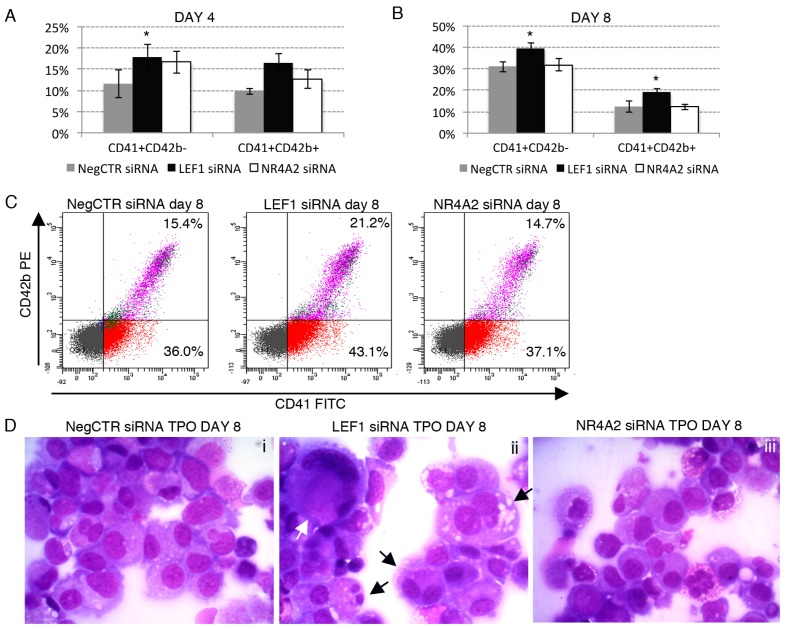
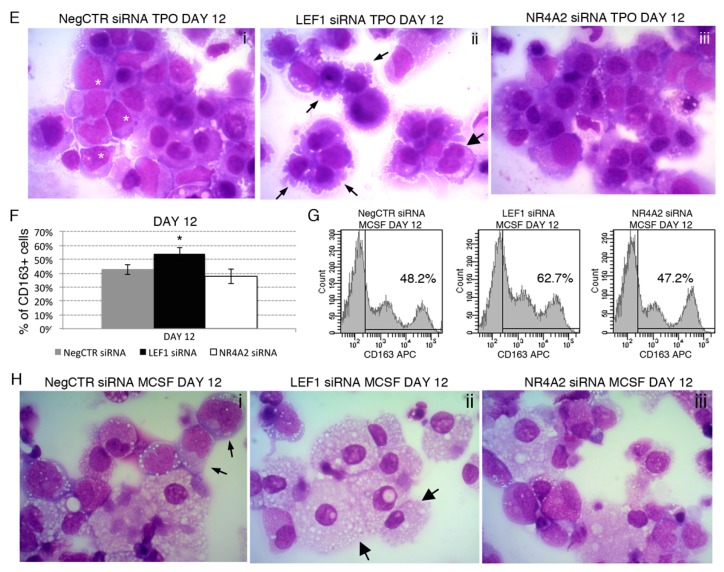
Figure 6.
Effects of LEF1 and NR4A2 silencing on megakaryocyte and macrophage differentiation. (A,B) Flow cytometric analysis (mean ± SEM; n = 3) of CD41 and CD42b expression at day 4 (A) and day 8 (B) of TPO-driven megakaryocyte unilineage culture post-nucleofection; (C) Representative dot plots for the flow cytometric detection of CD41 and CD42b differentiation markers at day 8 of megakaryocyte unilineage culture post-nucleofection; (D,E) Morphological analysis of NegCTR siRNA (i), LEF1 siRNA (ii) and NR4A2 siRNA (iii) cells after May–Grunwald–Giemsa staining at day 8 (D) and day 12 (E) of megakaryocyte unilineage culture post-nucleofection in a representative experiment. White asterisks indicate megakaryoblasts, that are immature cells of the megakaryocyte lineage characterized by a higher nucleus-to-cytoplasm ratio compared to mature megakaryocytes. The white arrow highlights a large megakaryocyte. Black thick arrows indicate polyploid megakaryocytes; black thin arrows indicate cells with cytoplasmic blebs, which are a feature of the megakaryocyte maturation in vitro. Magnification, ×1000; (F) Flow cytometric detection (mean ± SEM; n = 3) of the CD163 marker at day 12 of MCSF-driven monocyte/macrophage unilineage culture post-nucleofection; (G) Representative histograms for the flow cytometric detection of CD163 marker at day 12 of monocyte/macrophage unilineage culture post-nucleofection; (H) Morphological analysis of NegCTR siRNA (i), LEF1 siRNA (ii) and NR4A2 siRNA-transfected cells (iii) after May–Grunwald–Giemsa staining at day 12 of monocyte/macrophage unilineage culture post-nucleofection in a representative experiment. Thick arrows indicate macrophages; thin arrows indicate monocytes. Magnification, ×1000. Data are from n = 3 independent experiments performed with different healthy donor-derived cord blood units. * p ≤ 0.05 compared to NegCTR siRNA sample. Abbreviations: TPO, thrombopoietin; MCSF, monocyte colony-stimulating factor.