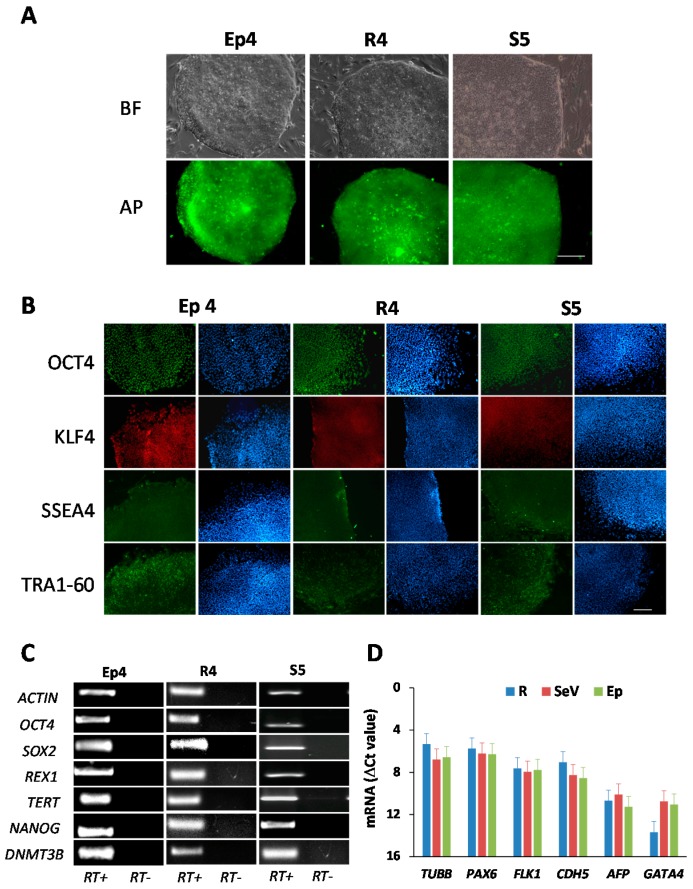
Figure 3.
Characterization of human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC) clones derived from human foreskin fibroblasts (BJ cells) by reprogramming with retroviral vectors (R), Sendai virus vectors (SeV), and episomal vectors (Ep). Data from a representative hiPSC clone for each reprogramming method are shown (R4, S5, Ep4). (A) Analysis of alkaline phosphatase (AP) expression in hiPSC clones; bright field (BF) images are also shown; (B) immunofluorescence staining of the pluripotent cell-specific markers OCT4, KLF4, SSEA4 and TRA1-60; DAPI in blue; (C) analysis of expression of the embryonic stem cell marker genes OCT4, SOX2, REX1, TERT, NANOG, DNMT3B by RT-PCR; (D) Embryoid Bodies (EBs) test: qRT-PCR analysis of differentiation markers of the three germ layers, i.e., ectoderm (PAX6 and TUBB), endoderm (AFP and GATA4), and mesoderm (FLK1 and CDH5), in EBs generated from iPSCs clones obtained with retroviral vector (R), Sendai virus vector (SeV), and episomal vector (Ep) transduction. Scale bars in panels (A,B) correspond to 200 µm.