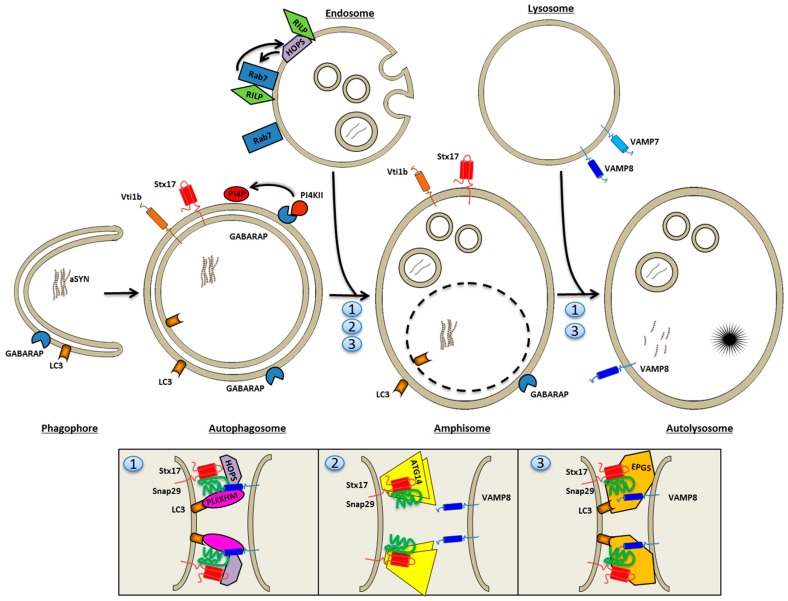
Figure 1.
Entry of autophagosomes into the endolysosomal system. The closed autophagosome is contained by two membranes, which allows the ultrastructural distinction of autophagosomes from any other organelle, as the outer membrane is lost upon the first fusion reaction. The autophagosomal Soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor-attachment protein receptor (SNARE) syntaxin17 and Atg14, which both influence later fusion reactions, are present on the phagosome Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase (PI4K)II and its lipid product phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate (PI4P) is specifically required for autophagososomes and late endosomes to form the hybrid organelle, an amphisome, in a fusion reaction mediated by Homotypic fusion and protein sorting (HOPS) and syntaxin17/Synaptosomal-associated protein (SNAP)29. Atg14 may primarily exert its function also at this stage. The subsequent fusion with lysosomes is also dependent on HOPS and syntaxin17/SNAP29, which partner up to form fusion competent trans-SNARE complexes with lysosomal SNARE Vesicle-associated membrane protein (VAMP)8. Alternative SNAREs for this fusion reaction are potentially v-SNARE Vesicle transport through interaction with t-SNAREs homolog 1B (Vti1b) and t-SNARE VAMP7. A number of factors have recently been identified that promote syntaxin17/SNAP29/VAMP8 interactions in different forms. ATG14 binds syntaxin17 directly, while Microtubule-associated proteins 1A/1B light chain 3B (LC3B) recruits both Pleckstrin homology domain-containing family M (PLEKHM) and Ectopic P-Granules Autophagy Protein 5 Homolog (EPG5) to the autophagosome. Here EPG5 (3) stabilizes the trans-SNARE complex with VAMP8, while PLEKHM (1) and ATG14 (2) interact with the bivalent SNARE pair syntaxin17/SNAP29.