Fig 2.
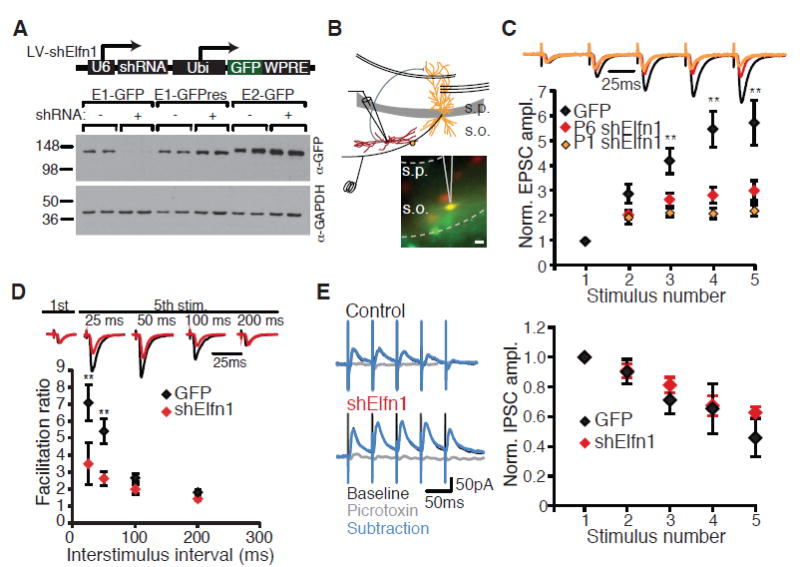
Elfn1 knockdown reduces short-term facilitation at CA1-O-LM synapses. (A) Western blot from human embryonic kidney (HEK) cells expressing Elfn1-GFP cotransfected with Elfn1 shRNA, blotted for GFP and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH). Knockdown is rescued by a point mutation in the target sequence of the Elfn1-GFP cDNA (E1-GFPres). (B) Recording configuration and epifluorescence images of tdTomato and GFP in stratum oriens. Scale bar, 20 mm. (C) (Top) Average postsynaptic response of control and shElfn1-expressing cells to five stimuli to the alveus at 20 Hz, normalized to the amplitude of the first EPSC. Black, GFP; red, shElfn1 at P6; orange, shElfn1 at P1. (Bottom) Population data for EPSC amplitude normalized to first EPSC. GFP, n = 13; P6 shElfn1, n = 20; P1 shElfn1, n = 7. (D) (Top) Example cells comparing first to fifth EPSC at different interstimulus intervals. (Bottom) Population data for facilitation ratio, calculated as the amplitude ratio of the fifth EPSC to the first EPSC. GFP, n = 12; shElfn1, n = 8. ** P < 0.01, analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey's honestly significant difference (HSD). (E) (Left) Example recordings of inhibitory synaptic responses in control and shElfn1-expressing cells to a 20-Hz stimulus before and after picrotoxin application. (Right) Average inhibitory postsynaptic current (IPSC) amplitude, normalized to the first IPSC amplitude. GFP, n = 7; shElfn1, n = 5. Error bars in all figures indicate SEM.
