Fig 4.
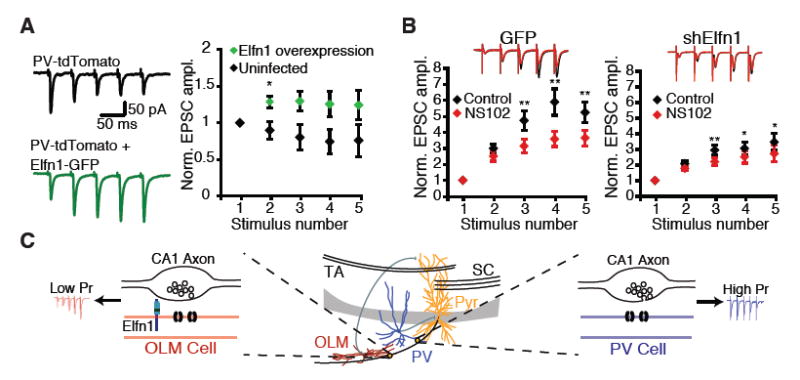
Elfn1 is sufficient to modulate CA1 outputs. (A) Lentivirus overexpressing Elfn1-GFP is injected into P5 PV∷tdTomato mouse pups. Stratum pyramidale or stratum oriens PV neurons in the infected area are targeted for recording. (Left) Response of control and shElfn1-expressing PV neurons to five stimuli delivered to the alveus at 20 Hz. (Right) Quantification of short-term plasticity in Elfn1 overexpressing PV cells. *P < 0.05 by Mann-Whitney U test. (B) (Right) Example recording and quantification of evoked EPSC in GFP-infected Sst neurons before and after application of the GluR6-selective kainate receptor antagonist, NS102 (20 mM). (Left) Average postsynaptic response of GFP-infected Sst interneurons before and after NS102, n = 8. (Right) Average postsynaptic response of shElfn1-infected Sst interneurons before and after NS102, n = 14. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01 by ANOVA with Tukey's post-hoc test. (C) Model of Elfn1 function at the synapse. In CA1, Elfn1 is selectively localized to excitatory synapses onto O-LM interneurons. Elfn1 signals transsynaptically to contacting CA1 axons to reduce probability of release and create a facilitating synapse.
