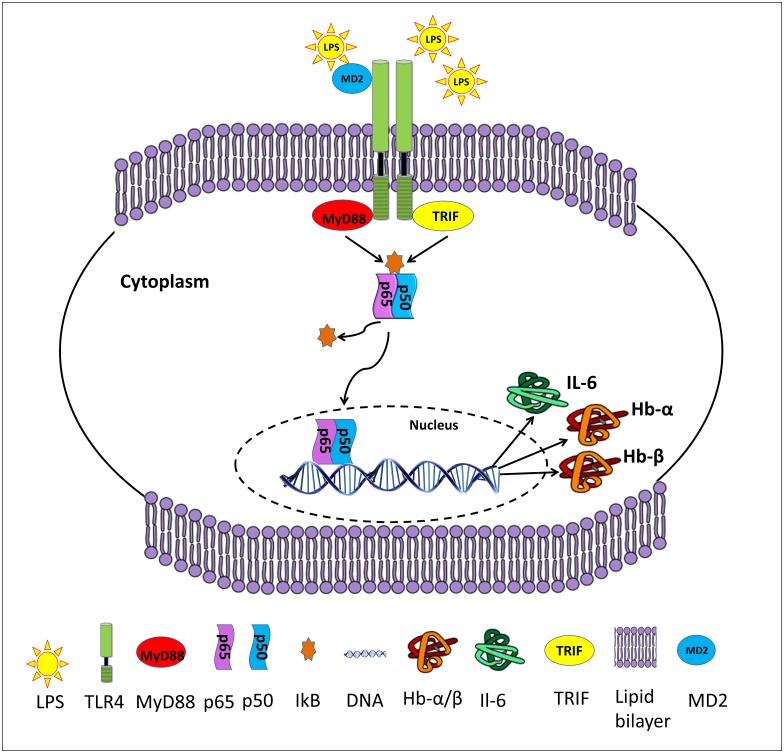
Fig 16. Hypothesized mechanism of Hb-α and Hb-β expression and their role in the function vaginal cells.
Stimulation of hPVECs with LPS up-regulates the expression TLR4, NF-κB, Hb-α, Hb-β and pro-inflammatory cytokine (e.g. IL-6). The co-receptor MD2 triggers interactions between the cell surface domain of TLR4 and LPS. Activated TLR4 interacts with cytoplasmic adaptor molecules MyD88 or TRIF which subsequently activates IKK complex. The IKK complex induces phosphorylation of IκB and its subsequent degradation liberates NF-κB and allows it to translocate into the nucleus where it can induce target gene expression including Hb-α, Hb-β and IL-6 etc and may contribute to pathogen clearance by enhancing local host immune responses in hPVECs. This figure represents the best-fit model for these effects.