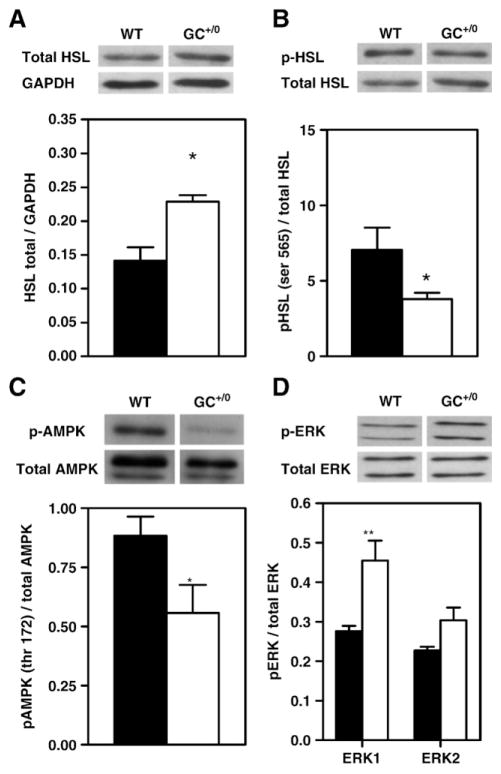
Fig. 4.
Mechanisms regulating lipolysis: levels and phosphorylation status of hormone sensitive lipase, AMP-activated kinase and extracellular signal regulated kinases 1/2 in WT and GC+/0 mouse hearts. Data are means±SEM of 4–5 (A, B and D) and 8 (C) freeze-clamped hearts of WT (solid bars) and GC+/0 (open bars) mouse hearts. Representative immunoblots using: (A) hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL) protein normalized to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), (B) anti-phospho-HSL (Ser-565) with anti-HSL serving as loading controls for total HSL protein total, (C) anti-phospho-αAMP-activated kinase (αAMPK; Thr-172) antibodies with anti-αAMPK antibodies serving as loading controls for total αAMPK protein, and (D) anti-phospho extracellular signal regulated kinases 1/2 (ERK1/2) with anti-ERK1/2 serving as loading controls for total ERK 1/2 protein. Densitometry of phosphorylated protein to total protein ratios from experiments performed on tissue homogenates extracts is shown. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 GC+/0 vs WT hearts.