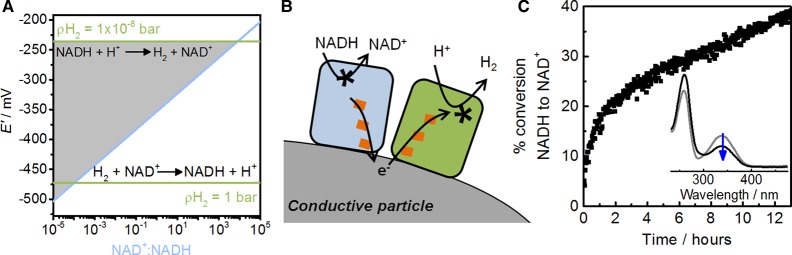
Figure 8. Oxidation of NADH to NAD+ coupled to H2 generation on carbon particles.
(A) Thermodynamics for H2 + NAD+ ↔ H+ + NADH at high and low H2 partial pressures (pH2) and a range of NAD+:NADH ratios. (B) Schematic representation of enzyme-modified particles for NADH oxidation and H2 production. (C) Conversion of NADH to NAD+ using H+ reduction as the electron sink at carbon black particles modified with E. coli Hyd2 [18] and the NAD+-reducing HoxHI64AYFU of R. eutropha in the presence of NADH (1 mM) at pH 8, 30°C.