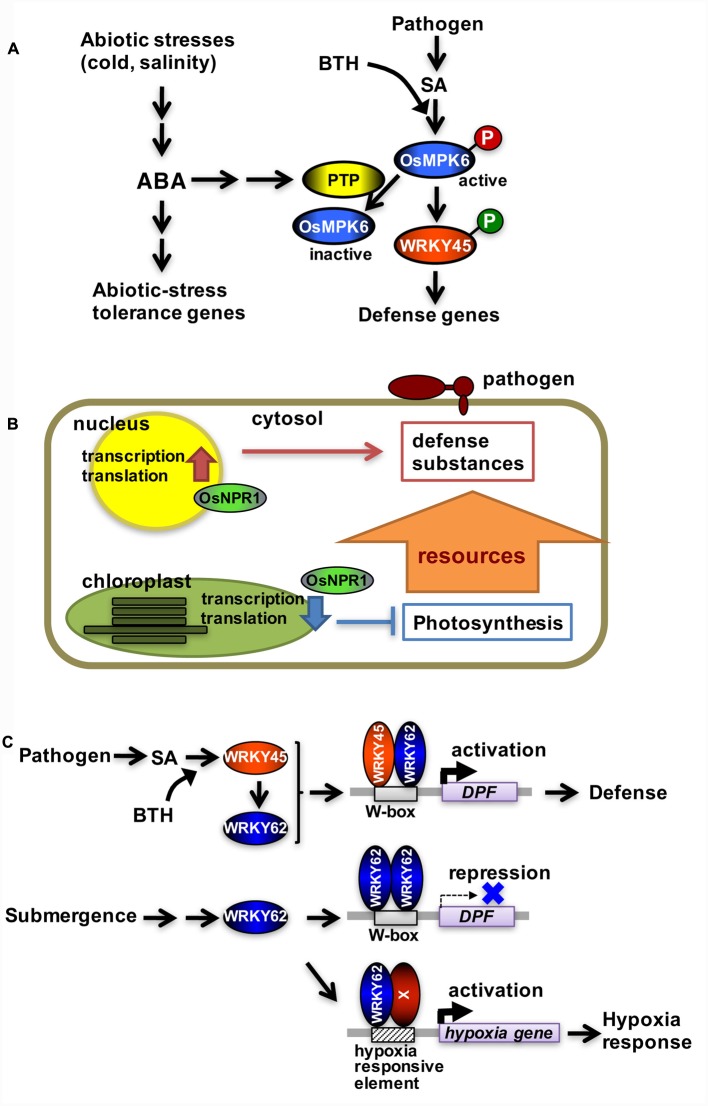
FIGURE 1.
Tradeoffs involving the salicylic acid pathway in rice. (A) Tradeoff between pathogen defense and abiotic stress tolerance mediated by protein tyrosine phosphatase. WRKY45 is phosphorylated and activated by OsMPK6 in response to chemical defense inducers. OsMPK6 is inactivated following tyrosine dephosphorylation by protein tyrosine phosphatase, which is mediated by ABA, in response to cold stress. This leads to hypo-phosphorylation and inactivation of WRKY45. (B) Tradeoff between pathogen defense and photosynthesis mediated by OsNPR1. OsNPR1 downregulates chloroplastic activity resulting in a decreased photosynthetic rate, while it upregulates the expression of defense genes. (C) Tradeoff between pathogen defense and submergence tolerance mediated by WRKY62. Following the activation of the salicylic acid pathway, WRKY45 and WRKY62 form heterodimers that activate DPF transcription. Upon submergence, only WRKY62 is produced, resulting in the formation of homodimers that repress DPF expression. Molecule X represents a presumptive transcription factor that binds to a hypoxia-responsive element in the promoter of hypoxia-responsive genes, possibly as a heterodimer with WRKY62.