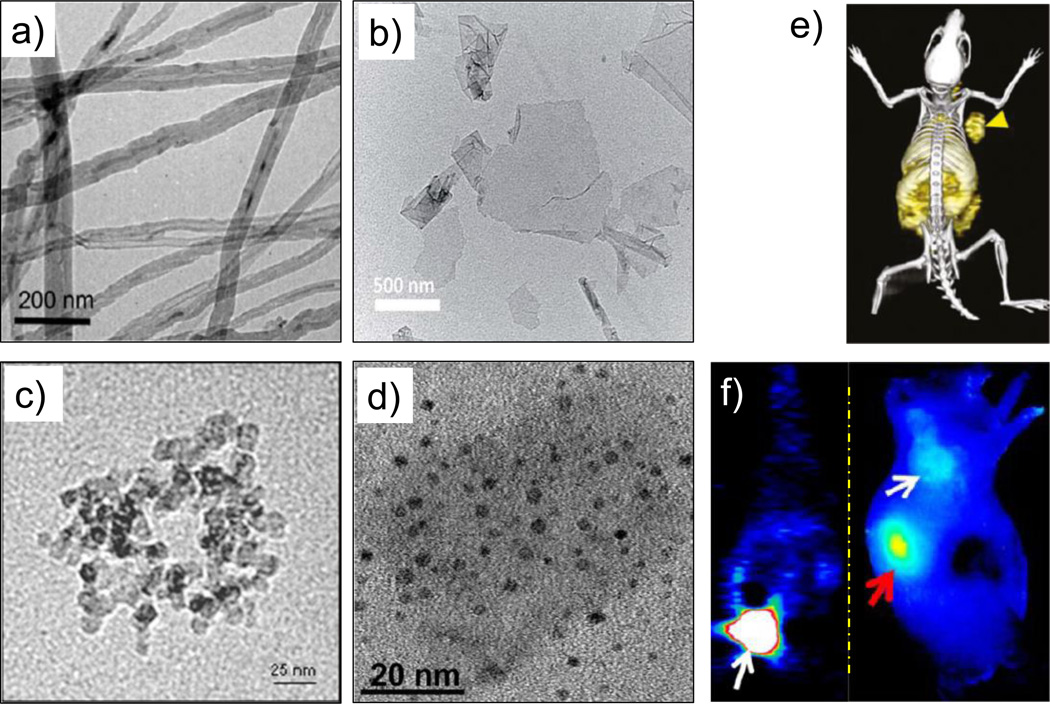
Figure 4.
TEM images of different (radiolabeled) carbon nanomaterials. (a) 14C-labeled multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Adapted with permission from [77]. Copyright by American Chemical Society. (b) Graphene oxide nanosheets. Adapted with permission from [95]. Copyright of the Royal Society of Chemistry. (c) Amine-modified nanodiamonds. Adapted with permission from [62]. (d) 800ZW-conjugated carbon nanodots. Adapted with permission from [98]. (e) In vivo PET/CT image of 64Cu-labeled GO conjugates in 4T1 murine breast tumor-bearing mice. Adapted with permission from [88]. (f) Coronal PET image 1 h p.i. of renal clearable 64Cu-labeled carbon nanodots; bladder indicated by white arrow (left), and NIR fluorescence image of SSC-7 tumor-bearing mice, 2 h p.i. of 800ZW-carbon nanodots; white arrow indicates the tumor and red arrow kidney (right). Adapted with permission from [98]. Copyright by American Chemical Society.