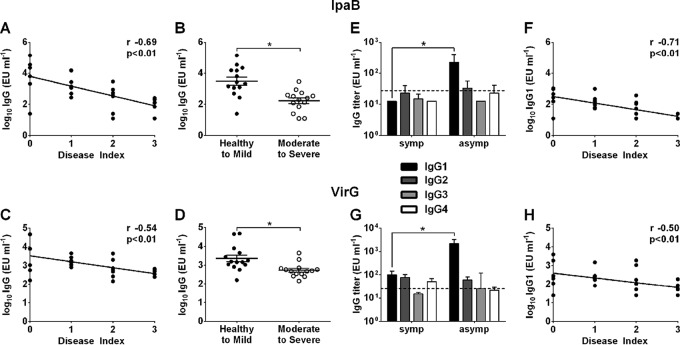
FIG 5.
Antigen-specific IgG levels are associated with decreased disease severity postinfection. (A and C) IpaB (A)- and VirG (C)-specific serum IgG titers in EcSf2a-2 vaccine recipients and nonvaccinated controls were correlated with disease index (DI) postchallenge by using Spearman's rank correlation (r and P values indicated on the plots). Individuals included in each DI category are as described in the legend to Fig. 3. (B and D) Titers were further grouped and compared based on disease severity (healthy to mild disease, DI of 0 or 1; moderate to severe disease, DI of 2 or 3) by using the Mann-Whitney U test. Asterisks indicate significant differences between groups at a P of ≤0.05. (E and G) IpaB (E)- and VirG (G)-specific IgG1 to -4 subclasses were measured in serum samples from volunteers who experienced severe disease (DI, 3) or remained healthy (DI, 0) postchallenge; a dashed line indicates the limit of detection of the assay. (F and H) IpaB (F)- and VirG (H)-specific IgG1 titers were correlated with DI postchallenge using Spearman's rank correlation (r and P values indicated on the plots).