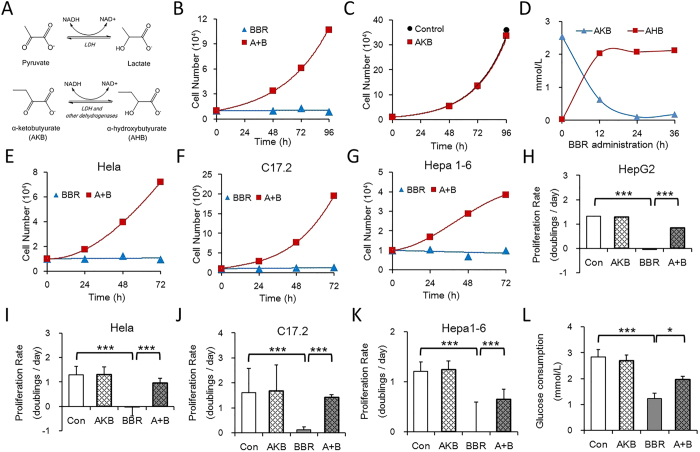
Figure 2. Exogenous Pyruvate or AKB serves as the alternative electron receptors as BBR blocks NAD+ regeneration.
(A) Pyruvate and AKB are substrates of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and other dehydrogenases, which receive electron from NADH and help to regenerate NAD+ (Referred from Sullivan et al.16). (B) Number of HepG2 cells with the indicated treatment. BBR 60 μmol/L, AKB (α-ketobutyrate) 1 mmol/L. (C) Number of HepG2 cells cultured with the indicated treatment. (D) Concentration of AKB and AHB in the media of HepG2 cells was determined over time by LC-MS/MS analysis. BBR 60 μmol/L. (E–G) Number of Hela, C17.2 and HepG2 cells with the indicated treatment. BBR: 60 μmol/L; A + B: BBR 60 μmol/L and AKB 1 mmol/L. (H–K) Proliferation rate of HepG2, Hela, C17.2 and Hepa1-6 cells with the indicated treatment. Con, control; BBR 60 μmol/L; AKB 1 mmol/L; A + B, BBR 60 μmol/L and AKB 1 mmol/L. Mean ± SEM; ***p < 0.001, n = 3. (L) Glucose consumption of HepG2 cells cultured with or without AKB and BBR. Glucose consumption is defined as the difference between the initial glucose concentration and the terminal glucose concentration in the medium. Con, control; BBR 60 μmol/L; AKB 1 mmol/L; A + B, BBR 60 μmol/L and AKB 1 mmol/L. Mean ± SEM; *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, n = 3.