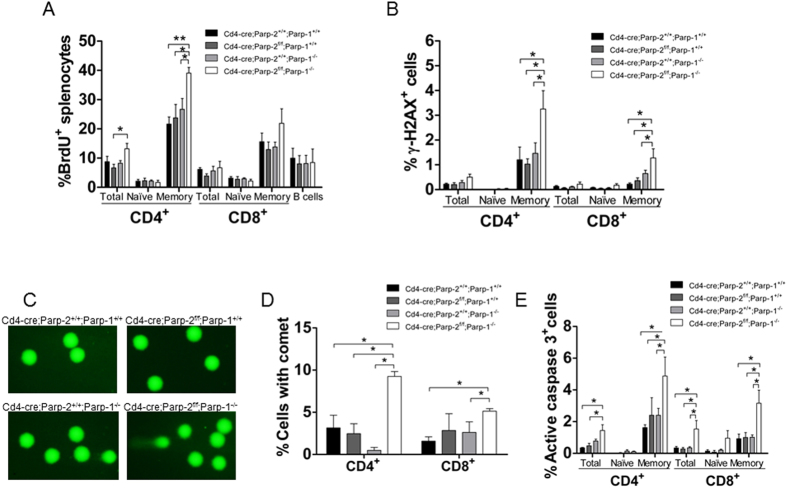
Figure 3. Effect of PARP-1/PARP-2 double deficiency on T-cell proliferation, DNA damage and apoptosis.
(A) In vivo proliferation of T-cell subsets. Eight-to-ten-week-old mice were i.p. injected with BrdU at 24 and 12 h before sacrifice. Cell suspensions from spleen were stained with anti-CD4, anti-CD8, anti-CD62L, anti-CD44 and anti-B220 to identify cell subsets, with anti-BrdU to identify cells synthesizing DNA and with DAPI to stain for the total DNA content in the cells. BrdU incorporation in each population was analysed by flow cytometry. Bars represent the mean ± SEM values of the percentage of BrdU+ cells. (B) Graph showing the mean ± SEM values of the percentage of γH2AX+ cells in each T-cell subset, determined by flow cytometry. (C) Representative image showing DNA damage in CD4+ splenic T-cells derived from mice of the indicated genotypes, visualized by the alkaline comet assay. (D) Graph showing the percentage of T-cells with comet. An average of 100 cells was scored from each mouse. (E) Graph showing the percentage of active caspase-3-positive T-cell in each subsets, determined by flow cytometry. Bars represent the mean ± SEM values obtained from at least 6 mice per genotype from two independent experiments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.