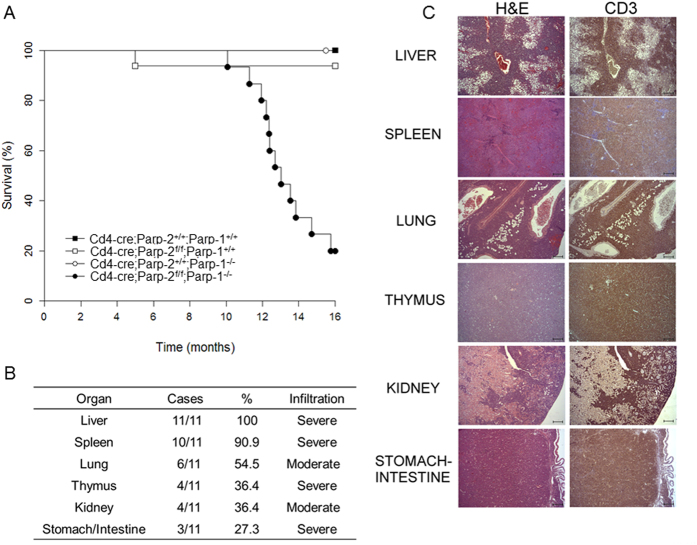
Figure 7. T-cell specific deletion of PARP-2 in a PARP-1-deficient background leads to death of mice with T-cell lymphomas.
(A) Kaplan-Meier survival curves for Cd4-cre;Parp-2+/+;Parp-1+/+(n = 9), Cd4-cre;Parp-2f/f;Parp-1+/+(n = 16), Cd4-cre;Parp-2+/+;Parp-1−/− (n = 8), and Cd4-cre;Parp-2f/f;Parp-1−/− (n = 15) mice. Percent survival is plotted as a function of time in months. The difference in survival between Cd4-cre;Parp-2f/f;Parp-1−/− and the other three genotypes was highly significant (p < 0.001) by log-rank test. (B) Summary of organs with highly invasive T-cell lymphoma cells. For evaluation of the infiltrative degree of tumors, a semi-quantitative scale comprising 4 grades was used: 0 (no infiltration), 1 (mild infiltration), 2 (moderate infiltration) and 3 (severe infiltration). The overall infiltrative value of each organ was established by calculation of the mean of all values obtained. (C) Hematoxylin and eosin (left panel) and anti-CD3 (right panel) staining of fixed tissue sections reveal that mortality of Cd4-cre;Parp-2f/f;Parp-1−/− mice is due to T-cell lymphomas. Scale bar: 0.2 mm.