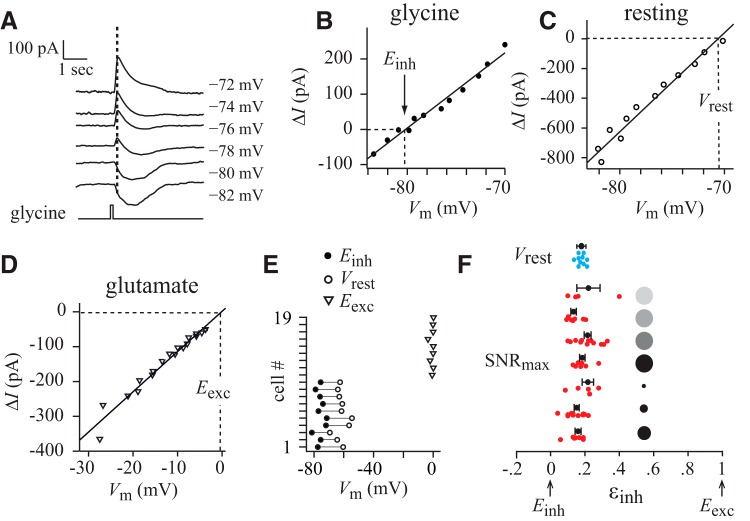
Figure 6.
The resting potential of the OFF delta cell sets up electrical forces on excitatory and disinhibitory conductances that are close to those that maximize SNR. A, Puffing glycine evoked an initial current due to chloride anions (Cl−) and a delayed current due to bicarbonate anions (HCO3−; Cordero-Erausquin et al., 2005; Price et al., 2009). The initial Cl− current was measured at the time indicated by the dashed line. B, I–V plot of Cl−. The membrane potential that zeroed out the current is Einh. C, I–V plot without transmitter to determine Vrest. D, I–V plot of glutamate currents to determine Eexc. E, Summary of perforated patch results: the absolute values of Einh and Vrest varied from cell to cell (Einh = −76.0 ± 1.0 mV, N = 10; Vrest = −61.5 ± 1.2 mV, N = 10; Eexc = −0.7 ± 0.4 mV, N = 9), but the electrical forces on excitation and disinhibition depend on voltage differences, which were more consistent (symbols connected by lines). F, The horizontal axis shows the balance of electrical forces on excitatory and disinhibitory conductances (εinh).The red dots represent individual cells that were recorded in whole-cell mode and show the balance of forces that maximizes SNR (SNRmax, from Fig. 3). The blue dots represent individual cells that were recorded in perforated patch mode and show the balance set by the resting potential (Vrest, calculated from the data in E). The balance of forces that maximizes SNR is close to the balance set by the resting potential.