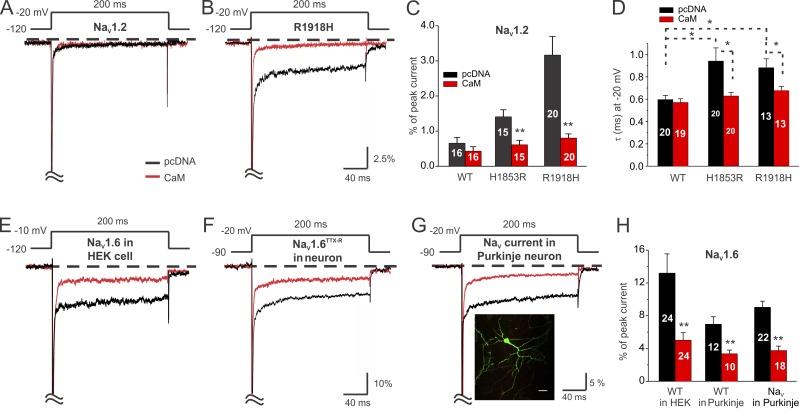
Figure 5.
ApoCaM regulates persistent Na+ current in neuronal NaV channels. (A and B) Exemplar traces for NaV1.2TTX-R (WT) and the NaV1.2 mutant R1918H showing increased persistent Na+ current for the R1918H mutant (but not for WT) and rescue by CaM overexpression for the R1918H mutant. (C) Summary data showing rescue by CaM for the NaV1.2 mutants H1853R and R1918H. (D) Summary data showing increased τ of inactivation and rescue by CaM for the NaV1.2 mutants H1853R and R1918H. (E) Exemplar traces for NaV1.6TTX-R (WT) expressed in HEK293T cells showing reduced persistent Na+ current by CaM overexpression. (F) Exemplar traces for NaV1.6TTX-R expressed in cultured cerebellar Purkinje neurons and reduced persistent Na+ current by CaM overexpression. (G) Exemplar traces of total NaV Na+ current in cultured cerebellar Purkinje neuron showing reduction in persistent Na+ current after CaM overexpression. The inset shows GFP-expressing cultured cerebellar Purkinje neuron. Bar, 20 µm. (H) Summary data for NaV1.6 expressed in HEK293T cells or in cultured cerebellar Purkinje neurons or total NaV Na+ current in cultured cerebellar Purkinje neurons. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01.