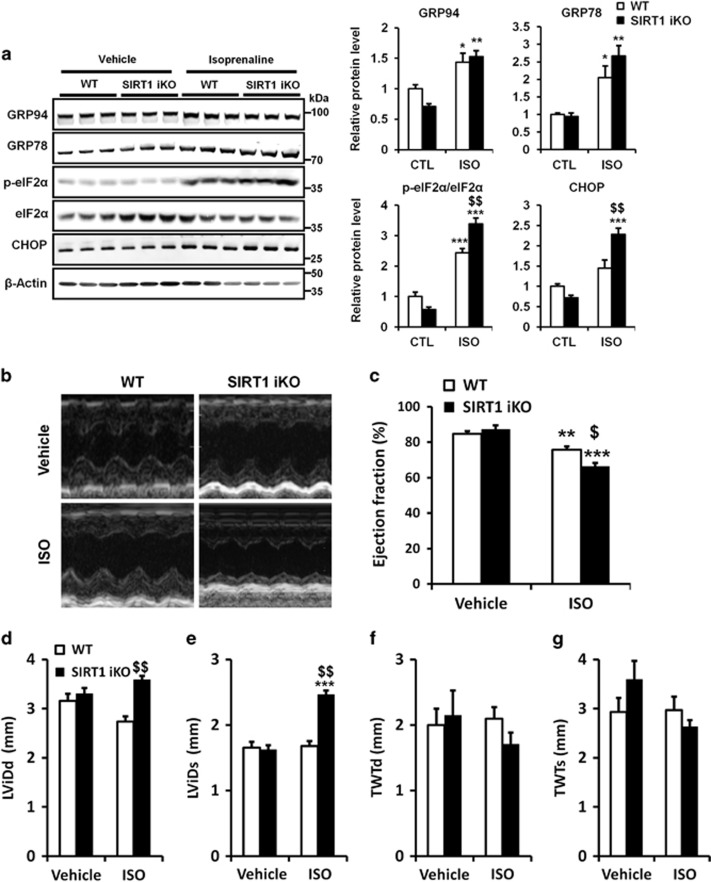
Figure 4.
Knockout of SIRT1 exacerbates PERK/eIF2α pathway activation and cardiac injury induced by ISO. (a) WT and SIRT1 iKO mice were injected subcutaneously with ISO (150 mg/kg) or vehicle (NaCl 0,9%) for 6 h and the levels of ER stress markers GRP94, GRP78, p-eIF2α, eIF2α and CHOP were analyzed by western blot in heart tissue. β-Actin was used as loading control. Relative expression of proteins (normalized to WT CTL) is presented in bar graphs. Error bars, S.E.M. (n=3). (b-g) Echocardiographic data were recorded 48 h after vehicle (NaCl 0,9%) or ISO treatment. (b) Representative images obtained by transthoracic echocardiography. (c) EF of WT and SIRT1 iKO mice after vehicle or ISO treatment. (n=5). (d) Left ventricular internal dimension (diastole), LVIDd, in vehicle or ISO-treated mice (n=5). (e) Left ventricular internal dimension (systole), LVIDs, in vehicle or ISO-treated mice (n= 5). (f) Total wall thickness (diastole), TWTd, in vehicle or ISO-treated mice (n=5). (g) Total wall thickness (systole), TWTs, in vehicle or ISO-treated mice (n=5). Results are presented as mean±S.E.M. **P<0.01, ***P<0.005 versus respective control. $P<0.05, $$P<0.01 versus WT ISO