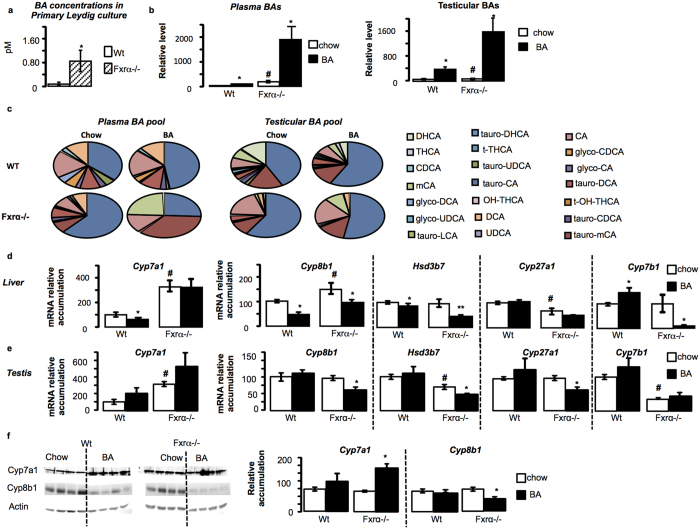
Figure 2. Fxrα deficiency alters BA homeostasis in liver and testis.
(a) BA levels produced by primary culture of wild-type (Wt) or Fxrα−/− Leydig cells 24 hours after serum starvation (n = 9 per genotype). (b) Plasma and testicular total bile acid levels in Wt and Fxrα−/− fed either chow-diet or BA-diet for 2 weeks (n = 5 per genotype). (c) Composition of plasma and testicular bile acid pool composition in wild-type and Fxrα−/− mice fed a control or BA-diet for 2 weeks (n = 5 per group). (d) Liver mRNA accumulation of Cyp7a1, Cyp8b1, Hsd3b7, Cyp27a1 and Cyp7b1 normalized to β-actin mRNA levels in wild-type and Fxrα−/− adult mice fed a control or BA-diet (n = 6–10 per group). (e) Testicular mRNA accumulation of Cyp7a1, Cyp8b1, Hsd3b7, Cyp27a1 and Cyp7b1 normalized to β-actin mRNA levels in wild-type and Fxrα−/− adult mice fed a control or BA-diet (n = 6–10 per group). (f) Testicular protein accumulation of Cyp7a1 and Cyp8b1 normalized to Actin levels in wild-type and Fxrα−/− adult mice fed a control or BA-diet (n = 6 per group). In all panels, wild-type control diet group was arbitrarily fixed at 100%. In all panels, data are expressed as means ± standard error of the mean. Statistical analysis: *P < 0.05. *Denotes significant difference between same genotype under different diets; #denotes significant difference between differents genotype under same diet exposure.