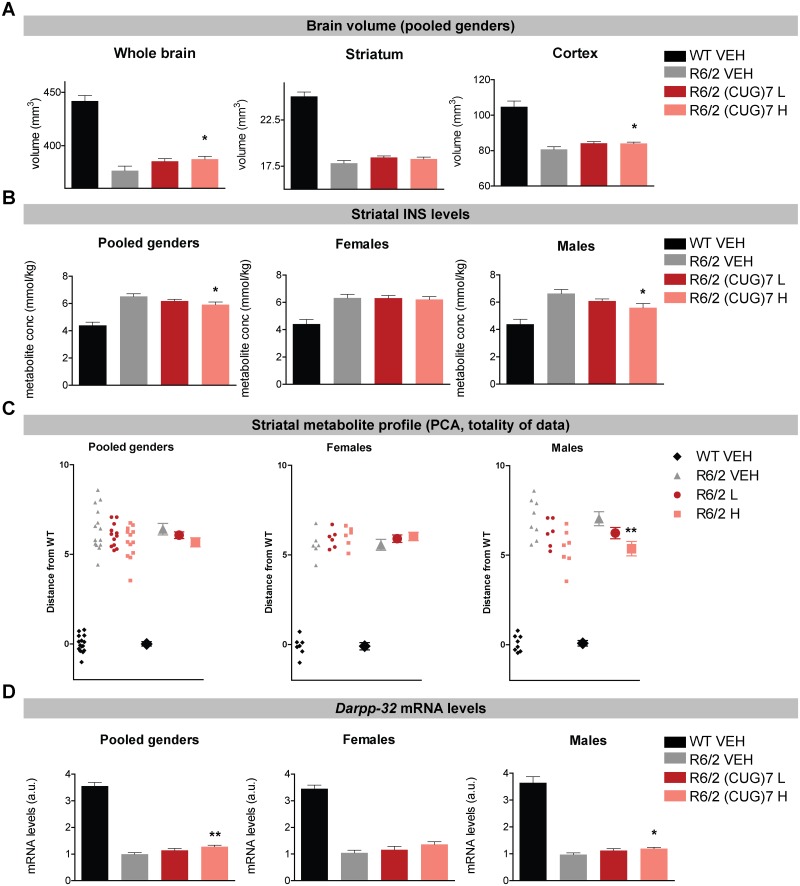
Fig 5. Effects of (CUG)7 on brain volume and neurochemical profile of striatum of R6/2 mice.
(A) MRI analysis of whole brain, cortical and striatal volume in (CUG)7-treated and VEH-treated R6/2 mice at 12 weeks of age in pooled genders (n = 12–15). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. ANOVA p-values to assess differences between groups were just above the p-value threshold of 0.05 in cortex and whole brain in pooled genders (cortex: p = 0.051; whole brain: p = 0.063). Using a 2-tailed t-test a significant increase in whole brain and cortical volume was observed for the high (CUG)7 dose groups compared to R6/2 VEH (*p<0.05) and a trend for the low dose group in cortex (p = 0.058). Results for females (n = 6–7) and males (n = 7–9) were not significant (data not shown). (B) The effect of (CUG)7-treatment on the concentrations of striatal metabolite myo-inositol (INS) in pooled genders (n = 12–15), female (n = 6–7) and male (n = 7–9) R6/2 mice at 12 weeks of age as measured by in vivo MR spectroscopy. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. ANOVA p-values to assess differences between groups were significant for males (p = 0.035) and displayed a trend for pooled genders (p = 0.070). Using a 2-tailed t-test a significant decrease in striatal INS levels were observed in the high dose treatment group in males and pooled genders (*p<0.05 compared to R6/2 VEH). (C) Principal component (PC) score of MRS data as distance from average of WT. PC scores for each individual mouse were projected onto a line connecting the averages of WT and R6/2 groups within the PC space, and then, PC score distances from WT along that line were obtained. This analysis gives an overall score (based on 16 separate metabolites) for individual mice (pooled genders: n = 12–15; females: n = 6–7 and males: n = 7–9). Significance was assessed using One Way ANOVA on R6/2 groups followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison posthoc test (**p<0.01 compared to VEH). A significant shift towards WTs was observed in males in the high dose treatment group. (D) Darpp-32 mRNA levels in striatum determined by RT-qPCR in pooled genders (n = 12–15), females (n = 6–7) and males (n = 7–9). Darpp-32 mRNA levels are expressed relative to levels after VEH-treatment and normalized against averaged expression levels of Ywhaz, Rab2 and Gapdh. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Using a 2-tailed t-test a significant increase in striatal Darpp-32 mRNA levels were observed in the high dose treatment group in pooled genders and males (*p < 0.05, **p<0.01 compared to R6/2 VEH). In females a similar trend was observed in the high dose group (p = 0.053).