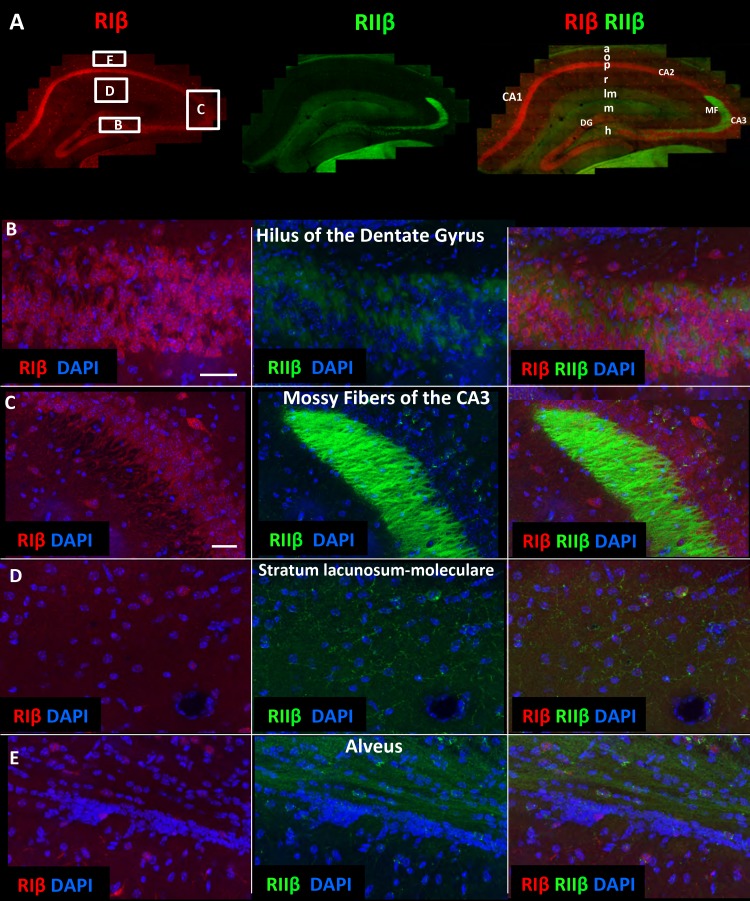
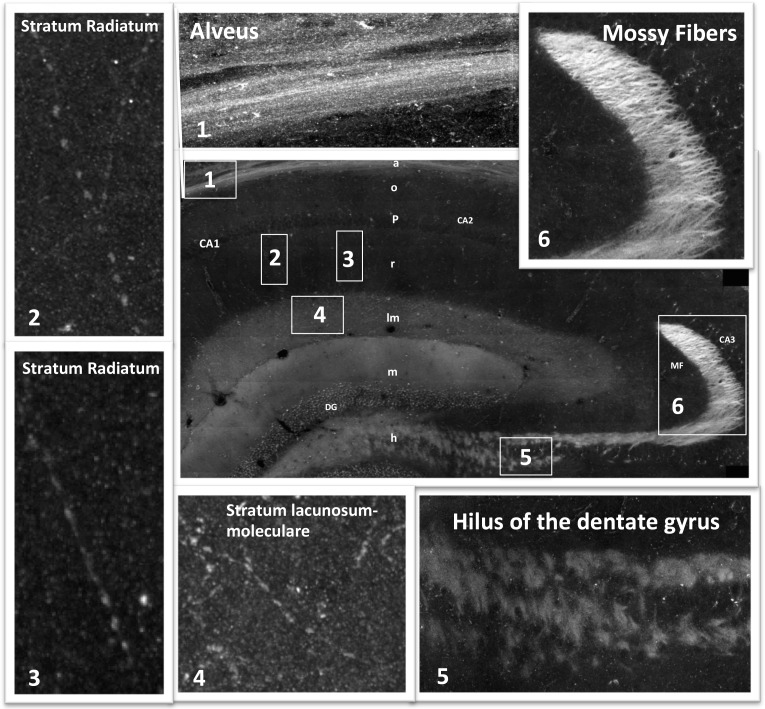
Figure 3. RIIβ is the predominant isoform in cell axons across various hippocampal subfields.
(A) A full representative mosaic of a coronal section through the dorsal hippocampus at reduced resolution. An overview of RIβ (red), RIIβ (green) and RIβ/RIIβ immunostaining at various subfields. The mosaic image is made up of 1,413 tiles from ten Z sections obtained using a 60x objective lens. The white box represents the area from which the (B–E) subfield full-resolution images were captured. (B) Hilus of dentate gyrus. (C) Mossy fiber of the CA3. (D) Stratum lacunosum-moleculare. (E) Alveus. Abbreviations: CA1, stratum oriens; g, granule cell layer (stratum granulosum); h, hilus proper; lm, stratum lacunosum-moleculare; m, dentate molecular layer (stratum moleculare); p, stratum pyramidale; r, stratum radiatum. Scale bar: 25 µm.