Fig. 2.
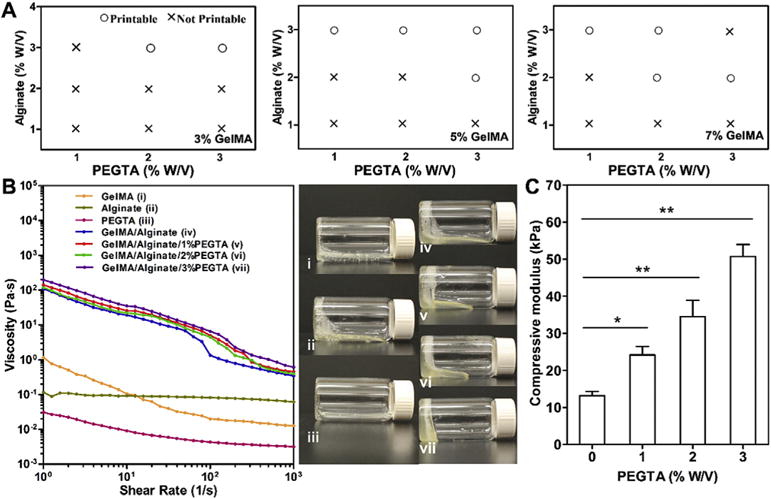
(A) Printability analysis of the blend bioinks. (B) Viscosity measurement and rheological behavior of 7% (w/v) GelMA, 3% (w/v) alginate, and 2% (w/v) PEGTA alone, as well as their mixtures at various concentrations at room temperature. The photographs on the right show the flow behavior of the respective bioinks at 10 min post transposing the containers. (C) Compressive moduli of bioinks composed of 7% (w/v) GelMA and 3% (w/v) alginate mixed with varied concentrations of PEGTA ranging from 0 to 3% (w/v) after exposure to 6.9 mW cm−2 UV light for 30 s (n = 6; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.001).
