Figure 2.
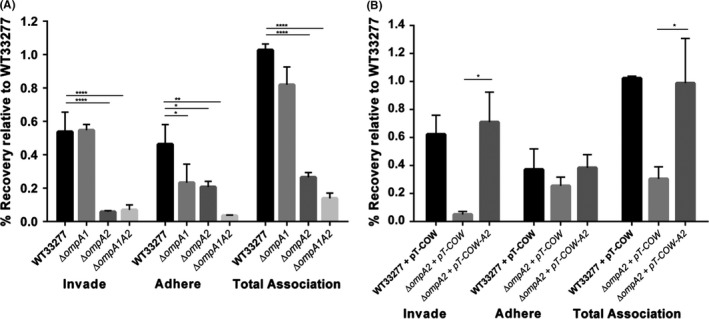
Bacterial adhesion and invasion of OK‐F6 monolayers by wild‐type, ∆ompA1, ∆ompA2 and ∆ompA1A2 mutants. P. gingivalis was incubated with a monolayer of OK‐F6 at a MOI 1:100 as described for invasion assays. Invasion was defined as the percentage of the inoculum protected from metronidazole killing. Total association was defined as the number of bacteria that have adhered to the OK‐F6 cell and invaded. Adherence was calculated from subtracting invasion CFUs from the total association. Each % value was determined by calculating the CFUs recovered as a percentage of the viability of that strain, and corrected to wild‐type P. gingivalis total association (=1). Wild‐type and mutant strains were evaluated for invasion and adherence efficiency (A), and the complemented ompA2 mutant (B) assessed. Statistical significance was determined by students’ t‐test and designated as *p < .05, **p < .01, **** p < .0001 (n = 3). Error bars are ± SEM
