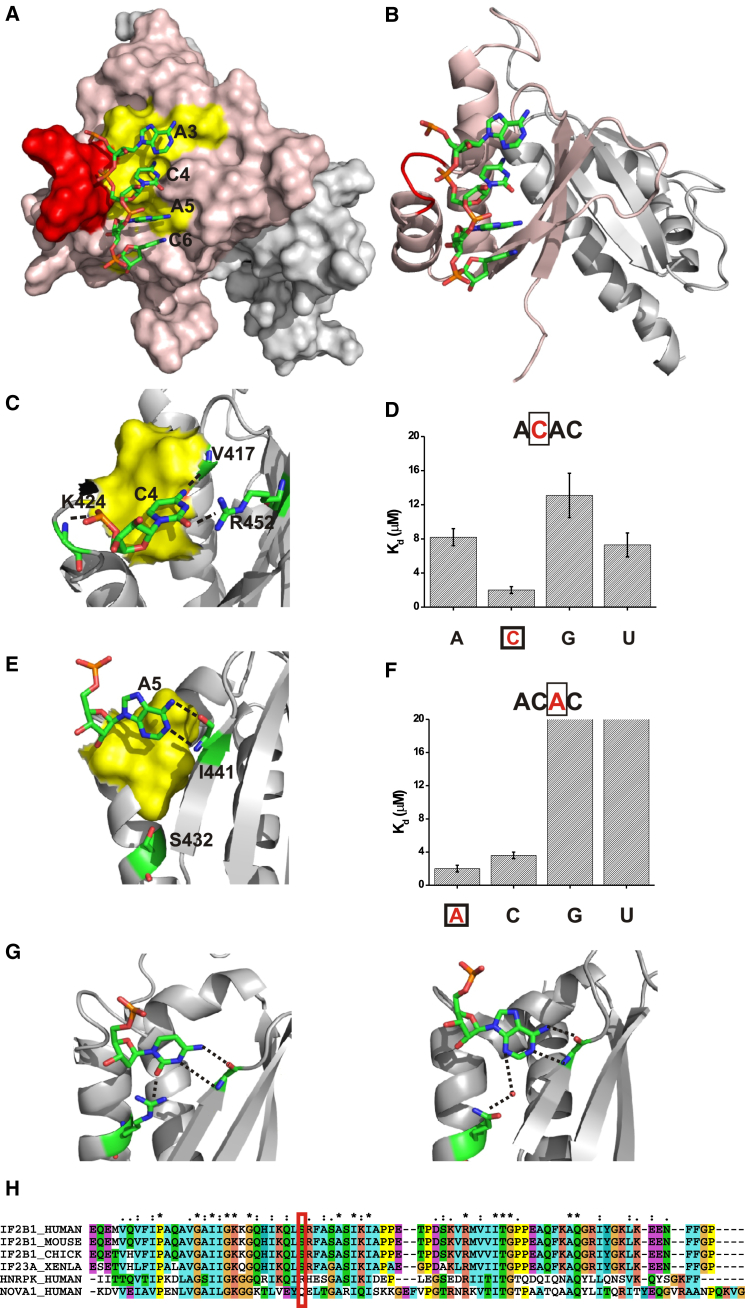
Figure 2.
Structure and Specificity of the KH3-RNA Complex
(A) The KH3-RNA complex. Surface representation of the bound KH3-KH4DD protein and stick representation of the cognate ACAC sequence. The RNA is colored by atom type, whereas the KH3 protein surface is pink, except for the GxxG loop (red) and the hydrophobic groove (yellow). The KH4 protein, in the back, is colored in gray.
(B) The same complex is represented using a cartoon for the protein. KH3 is in pink, KH4 in grey.
(C) Detail of the structure: the C4-KH3 interaction. Cartoon representation of the bound KH3 secondary structure. The KH3 hydrophobic surface contacting the RNA is in yellow, whereas the residues H-bonded to the RNA and the RNA itself are displayed using a stick representation.
(D) Kds of the protein in complex with, from left to right, the CAAAC, CACAC (wild type [wt]), CAGAC, and CAUAC RNAs. Kds were measured using ITC. Raw and fitted data can be found in Figure S4, together with more experimental details. Kd values are represented as a histogram and are capped at 20 μM in the figure to represent the approximate limit at which an accurate figure can be obtained. Data fitting error is reported. All experiments were repeated twice.
(E) Detail of the structure: the A5-KH3 interaction. Color coding and representation as in (C).
(F) Kds of the protein in complex with, left to right, CACAC (wt), CACCC, CACGC, and CACUC. ITC experiments were performed and analyzed as in (D).
(G) Comparison of the position 3 nucleobase H-bonding in the hnRNP K KH3-RNA (left) and Nova KH3-RNA (right). Regardless of the identity of the nucleobase, a third H-bond is observed with equivalent residues in helix 2, which is either an R (for C) or a Q (for A).
(H) Alignment of the ZBP1 KH3 sequences in vertebrates with the Nova-1 KH3 and hnRNPK sequences (ClustalX). The residue in helix 2 H-bonded to A5 is boxed in red. See also Figures S1–S5.