Figure 7.
Inhibiting IP3 Receptor-Mediated Ca2+ Delivery to Mitochondria Abrogates the Effects of VAPB and PTPIP51 Overexpression on Autophagosome Formation
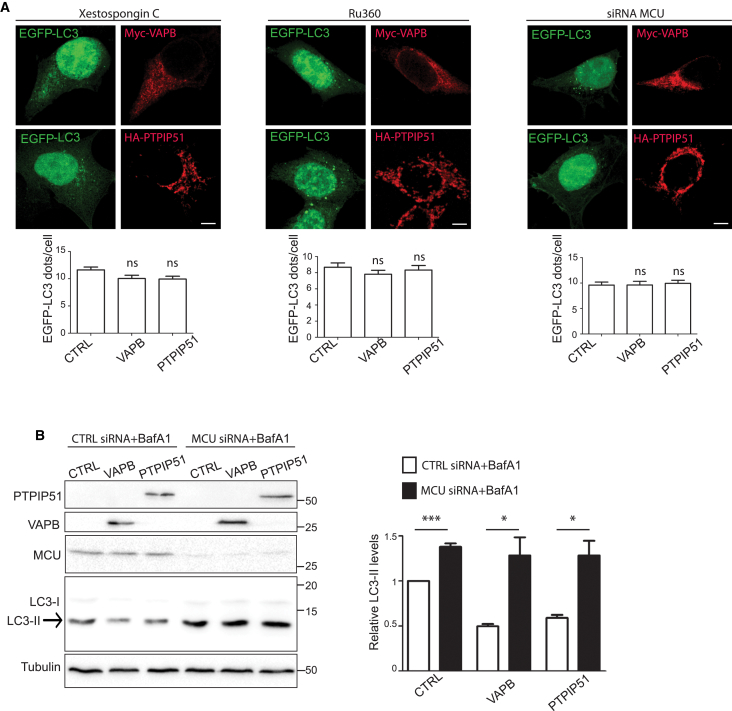
(A) Representative images of HEK293 cells co-transfected with EGFP-LC3 and either myc-VAPB or HA-PTPIP51 and treated with either the IP3 receptor inhibitor Xestospongin C, the mitochondrial Ca2+ uniporter (MCU) blocker Ruthenium-360 (Ru360), or MCU siRNAs. For MCU siRNAs, cells were first treated with siRNAs and then transfected with plasmids. Cells were immunostained for VAPB and PTPIP51 via their epitope tags and LC3 visualized via the EGFP tag. The scale bars represent 10 μm. Bar charts show numbers of EGFP-LC3 dots per cell in the different experiments. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA. n = 118–187 cells in three or four independent experiments. Error bars are SEM.
(B) siRNA loss of MCU increases LC3-II levels and abrogates the effects of VAPB and PTPIP51 overexpression on LC3-II levels in bafilomycin-A1-treated HeLa cells. Cells were treated with CTRL or MCU siRNAs, transfected with either myc-VAPB or HA-PTPIP51, and treated with bafilomycin A1 (BafA1) as indicated. Samples were then probed on immunoblots for LC3, MCU, VAPB, PTPIP51, and α-tubulin as a loading control. VAPB and PTPIP51 were detected via their epitope tags. Both LC3-I and LC3-II isoforms are shown; arrow indicates LC3-II isoform. Molecular mass markers are indicated in kD. The bar chart shows relative LC3-II levels following quantification of signals from immunoblots. LC3-II levels were normalized to α-tubulin signals. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post hoc test; n = 3. Error bars are SEM; ∗p ≤ 0.05; ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001.
See also Figure S4.