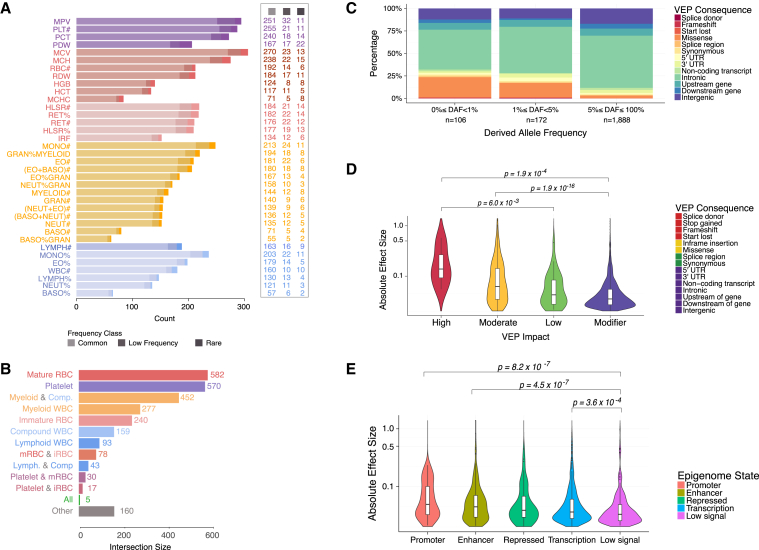
Figure 3.
Distribution of Genetic Effects and Variant Consequences
(A) Number of conditionally independent genetic associations categorized by blood cell index and by MAF range.
(B) Summary of sizes of subsets of sentinel variants categorized by cell types of associated indices, showing that most associations are cell-type-specific. Each bar counts the number of sentinel variants associated with and only with the blood index class(es) shown. (mRBC, Mature RBC; iRBC, Immature RBC; Lymph, Lymphoid WBC; Comp, Compound WBC; All, Intersection of all blood index classes. “Other” counts variants uncounted by the other bars.) See Table S1 for blood index classification.
(C) Bar plot showing the proportions of variants categorized by VEP consequence stratified by derived allele frequency (DAF) range.
(D and E) Violin plots showing the distribution of the absolute value of the estimated effect size stratified by VEP impact categories (D) or cell-matched chromatin segmentation states (E). p values correspond to Mann-Whitney-Wilcoxon tests comparing the distributions indicated.
See also Table S4.