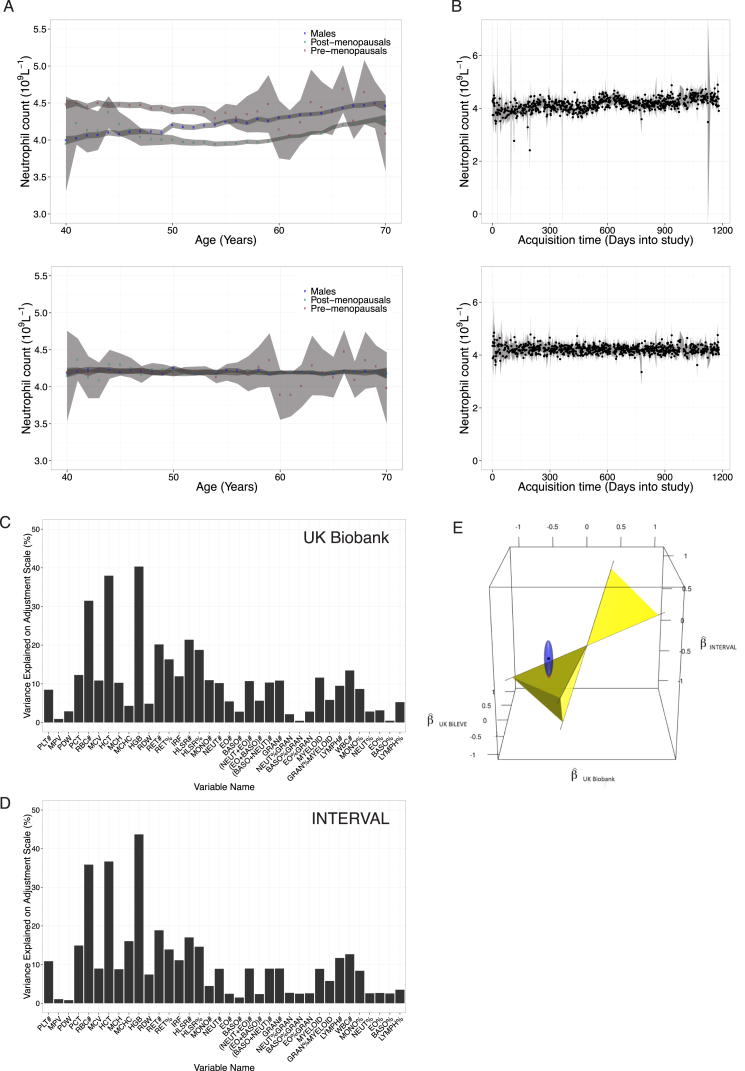
Figure S2.
Adjustments for Sex and for Biological and Environmental Covariates Affecting Full Blood Count Measurements, Related to Figure 1, Tables S1 and S2, and the STAR Methods
(A) The dependence of mean neutrophil count on sex and menopause status in the UK Biobank data adjusted for technical effects. The top plot is obtained using the raw data while the bottom plot is obtained adjusting the data for menopause and sex effects showing the elimination of the variance these covariates explain.
(B) Day averaged measurements of neutrophil count taken from a single instrument over the course of the UK Biobank baseline recruitment. There is a long run upward drift in the average count over time. Seasonal oscillation in the average counts is also visible. The top plot is obtained using the raw data while the bottom plot is obtained using the technically adjusted data, showing the elimination of drift and seasonal oscillation.
(C) Percentage of variance of UK Biobank traits explained (on the relevant adjustment scale) by sex and covariates affecting full blood counts, including age, menopausal status, smoking and alcohol variables.
(D) As for (C) except for INTERVAL traits.
(E) Illustration of the method used to determine the weight of evidence that heterogeneity in effect sizes across the three studies exceeded a tolerance criterion. The axes represent effect sizes in UK Biobank, INTERVAL and UK BiLEVE. The black dot represents the vector of study specific effect size estimates (UK Biobank,INTERVAL, UK BiLEVE,) for a variant. If the dot lies inside the infinite yellow double-pyramid (defined by three planes intersecting the origin, each normal to one of n1 = (1,−1/4, −1/4), n2 = (−1/4,1, −1/4), n3 = (−1/4,−1/4, 1)) we consider that there is no evidence of between study heterogeneity. If the black dot lies outside the yellow double-pyramid we measure the strength of evidence for heterogeneity as the distance between the black dot and the nearest point on the surface of the pyramid (red dot), with distances scaled to account for the standard errors of the study specific estimators. The nearest point on the pyramid is thus defined as the point in the smallest confidence surface for the estimators that intersects the pyramid (blue ellipsoid). We thresholded the distance score at 5.2 and filtered all variant-blood index pairs exceeding the score from further analysis.