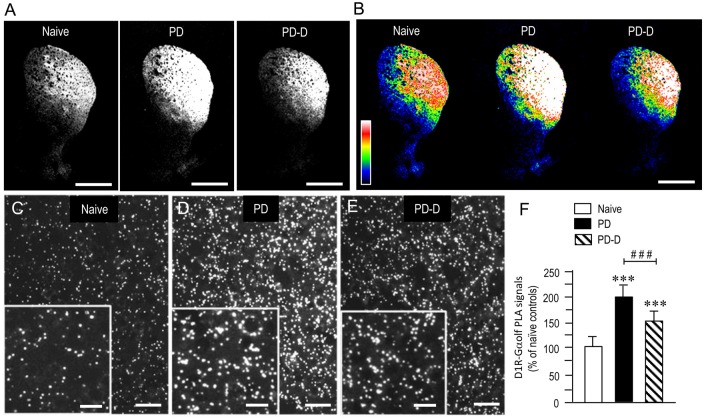
Figure 5.
Dopaminergic regulation of striatal levels of Gαolf proteins in close proximity to D1R proteins. Dual-antigen recognition in situ PLA used to detect Gαolf proteins in proximity to D1R proteins (D1R-Gαolf) was carried out on normal hemispheres of naïve controls and on lesioned hemispheres from 6-OHDA-lesioned mice treated with daily injections of benserazide alone for 10 days (PD model) and from 6-OHDA-lesioned mice that received daily injections of benserazide and L-DOPA for 10 days and exhibited dyskinesia (PD-D model). (A,B) Representative photomicrographs of striatal expression of D1R-Gαolf PLA signals in normal and lesioned hemispheres from PD and PD-D mice (A), and their graded color-converted images (B). (C–E) Representative photomicrographs of the DL striatum stained with the in situ PLA for D1R-Gαolf from naïve control (C), PD (D) and PD-D (E) mice. Their higher-magnification images are also shown in the insets in (C–E). (F) Optical density quantification of D1R-Gαolf PLA signals in the DL striatum from PD (n = 10) and PD-D (n = 10) mice. Data are expressed as percentage of naïve control mice (n = 10) and are means ± SEM. ***P < 0.001 vs. normal controls; ###P < 0.001 vs. PD; one-way ANOVA (F(2,27) = 107.2) followed by Bonferroni’s test. Scale bars: (A,B) = 2 mm; (C–E) = 25 μm; insets in (C–E) = 10 μm.