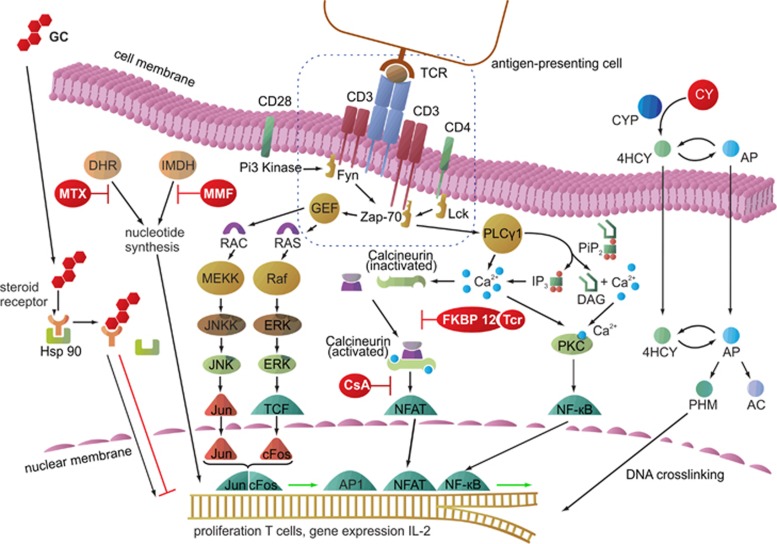
Figure 1.
Cellular pathways of commonly used clinical immunosuppressive agents. GCs reach the nucleus via diffusion through the cell membrane and form a complex after binding to a steroid receptor protein following separation from Hsp 90. The complex binds to specific DNA sequences and affects the transcription of a variety of genes. MTX inhibits DHR, which is necessary for nucleotide synthesis, thereby constraining cell division. MMF blocks the IMDH, which is also required for nucleotide synthesis. CY is metabolized by CYP450 to 4HCY, which interconverts to AP. Both tautomers are able to passively diffuse into cells. Then, AP is converted to AC and PHM, which possesses DNA-crosslinking properties. CsA binds to an intracellular immunophilin and blocks calcineurin to enable NFATs, whereas tacrolimus (Tcr) binds to the intracellular FK506 binding protein (FKBP) and also inhibits NFAT activation, ultimately preventing cell proliferation. AC, acrolein; AP, aldophosphamide; CsA, cyclosporin A; CY, cyclophosphamide; CYP450, cytochrome P450; DAG, diacylglycerol; DHR, dihydrofolate reductase; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; Fyn, tyrosine-protein kinase; GEF, guanine-nucleotide exchanging factor; GH, glucocorticoid; 4HCY, 4-hydroxyphosphamide; Hsp 90, heat-shock protein 90; IP3, inositol triphosphate; IMDH, inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; JNKK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase kinase; RAC, guanosine triphosphate; RAS, guanosine-nucleotide-binding protein; Lck, lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase; MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; MEKK, serine/threonine-specific protein kinase; MMF, mycophenolate mofetil; MTX, methotrexate; NF-κB, nuclear factor 'κ-light-chain enhancer' of activated B cells; NFAT, nuclear factor of activated T cell; PHM, phosphoramide mustard; Pip2, phosphatidyl inositol bisphosphate; PKC, protein kinase C; PLCγ, phospholipase C-γ RAF, serine/threonine-specific protein kinase; TCF, transcription factor; TCR, T-cell receptor; Zap-70, zeta-chain-associated protein kinase 70.