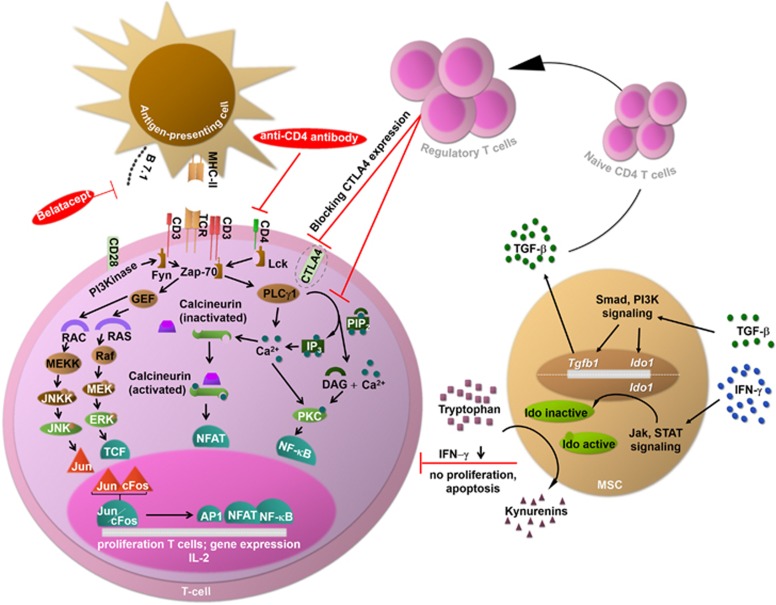
Figure 2.
Mechanisms of action of the experimental approaches. Experimental approaches for immunosuppression comprise MSCs, Tregs, anti-CD4 antibodies and substances blocking costimulatory pathways. MSCs act on CD4+ T cells via IFN-γ and TGF-β. First, the IFN-γ concentration is reduced by MSCs, inhibiting proliferation and inducing the apoptosis of T cells. Second, the TGF-β concentration is increased by MSCs, driving the differentiation of naive CD4+ T cells into Tregs. In turn, Tregs directly inhibit CD4+ T-cell proliferation via the suppression of Ca2+-dependent pathways and indirectly act by downregulating costimulatory molecules such as CTLA4. Finally, anti-CD4 antibodies and substances blocking costimulatory pathways (belatacept) impair T-cell activation. CTLA4, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4; DAG, diacylglycerol; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; Fyn, tyrosine-protein kinase; Ido, indolamine-2,3-dioxygenase; GEF, guanine-nucleotide exchanging factor; IFN-γ, interferon-γ IP3, inositol triphosphate; Jak, Janus kinase; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; JNKK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase kinase; Lck, lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase; MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; MEKK, serine/threonine-specific protein kinase; MSC, mesenchymal stem cell; NF-κB, nuclear factor 'κ light-chain enhancer' of activated B cells; Pip2, phosphatidyl inositol bisphosphate; PI3K/Pi3 kinase, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PLCγ, phospholipase; PKC, protein kinase C; RAC, guanosine triphosphate; RAF, serine/threonine-specific protein kinase; RAS, guanosine-nucleotide-binding protein; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; TCF, transcription factor; TCR, T-cell receptor; TGF-β, tumor growth factor-β Tregs, regulatory T cells; Zap-70, zeta-chain-associated protein kinase 70.