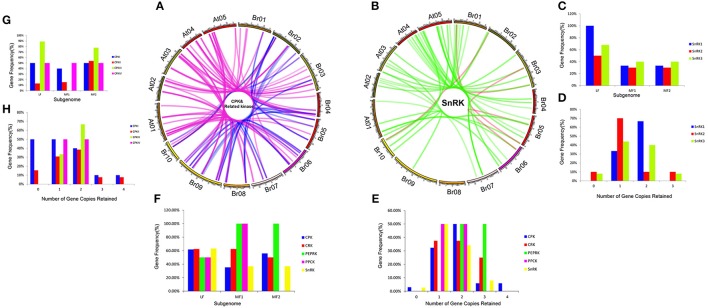
Figure 4.
CDPK-SnRK homologous genes in the segmental syntenic regions of the genomes of Brassica rapa and Arabidopsis thaliana and their different retention. (A) CPK, CRK, PEPRK, and PPCK syntenic gene lines are shown between the 10 B. rapa chromosomes (Br01-Br10) and the five Ar. Thaliana chromosomes (At01-At05). The pink lines represent the syntenic gene pairs between Chinese cabbage and Arabidopsis; the blue lines represent the syntenic genes in Chinese cabbage. (B) SnRK syntenic gene lines are shown between the 10 B. rapa chromosomes and the five A. thaliana chromosomes. The green lines represent the syntenic genes pairs between Chinese cabbage and Arabidopsis; the red lines represent the syntenic genes in Chinese cabbage. (C) Retention of homoeologs of SnRK genes in the three subgenomes (LF, MF1, and MF2) in B. rapa. LF: least fractionized subgenome; MF1: moderately fractionized subgenome; MF2: most fractionized subgenome. (D) Copy numbers of SnRK genes after genome triplication and fractionation in B. rapa. (E) Copy numbers of CDPK-SnRK genes after genome triplication and fractionation in B. rapa. (F) Retention of homoeologs of CDPK-SnRK genes in the three subgenomes (LF, MF1, and MF2) in B. rapa. (G) Retention of homoeologs of CPK genes in the three subgenomes (LF, MF1, and MF2) in B. rapa. (H) Copy numbers of CPK genes after genome triplication and fractionation in B. rapa.