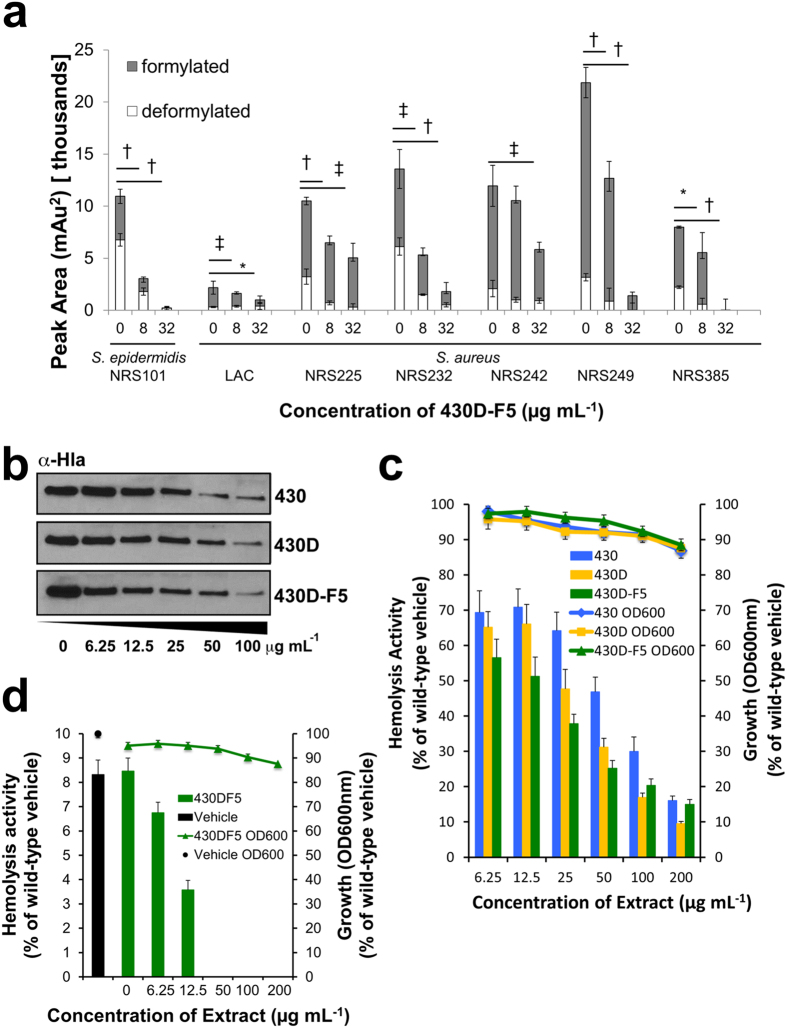
Figure 4. 430D-F5 inhibits δ-toxin and α-hemolysin production in a dose-dependent manner.
(a) Levels of δ-toxin were quantified by HPLC analysis of culture supernatant following treatment with sub-MIC50 concentrations of 430D-F5. S. epidermidis strain is NRS101, all others are S. aureus. Refer to Suppl. Table 5 for full strain details. Results are expressed as the peak area, normalized for optical density (600 nm) at the time of supernatant harvest. Statistical significance is denoted as *P-value < 0.05, ‡P < 0.01, †P < 0.001. (b) Western blot analysis displays dose dependent inhibition of α-hemolysin production in USA300 strain LAC (c) Red blood cells exposed to supernatants from 430, 430D and 430D-F5 treated cultures demonstrate dose-dependent inhibition of hemolysis by S. aureus (LAC) toxins. All treatments are significant in comparison to wild type vehicle control at P < 0.001. (d) Dose dependent reduction in hemolysis is also evident in 430D-F5 treated supernatants from a hla mutant strain (AH1589). All treatments are significant in comparison to wild type vehicle control at P < 0.001. No significant growth inhibition in comparison to the vehicle control was observed.