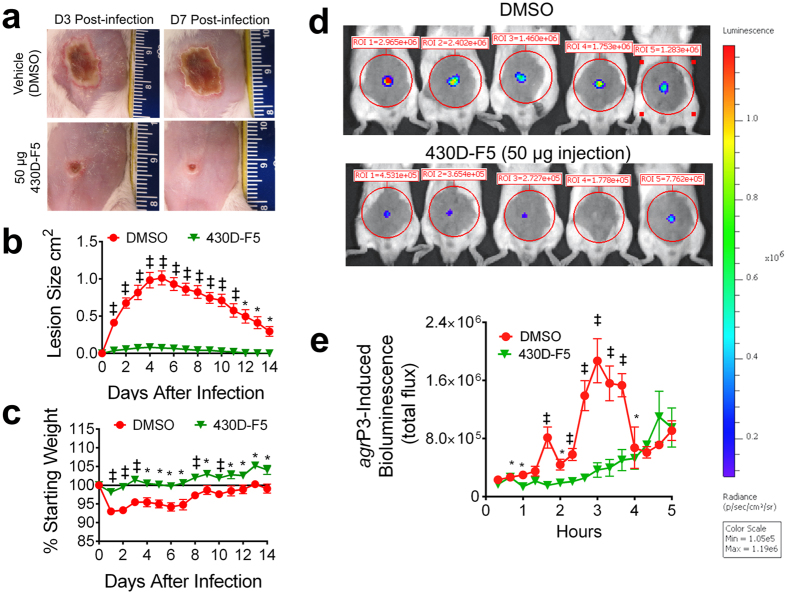
Figure 8. 430D-F5 mediates quorum quenching in vivo and attenuates MRSA-induced dermatopathology in a murine model of skin and soft tissue infection.
(a) BALB/c mice were intradermally challenged with an inoculum mixture containing 1 × 108 CFUs of MRSA (LAC) along with either 50 μg of 430D-F5 or the vehicle control (DMSO). Representative images of the resulting cutaneous injuries sustained in 430D-F5 and vehicle control mice are shown for days 3 and 7 post-infection (scale in cm). (b) A single 50 μg dose of 430D-F5 profoundly attenuates dermatopathology following cutaneous MRSA challenge. (c) 430D-F5 reduces morbidity as measured by animal weight. (d) To determine if 430D-F5 inhibits quorum sensing in vivo, mice were challenged intradermally with an agr P3-lux reporter strain (AH2759) +/− 430D-F5 and agr-driven bioluminescence was measured at the indicated time points via IVIS imaging. Quorum sensing peaks at 3 hr post injection, and a single injection of 430D-F5 exhibits significant inhibition of the system for the first 4 h post-injection. (e) In vivo monitoring demonstrates that 430D-F5 quenches quorum sensing signaling. This image was taken at 3 hr post challenge, during the peak period for agr activity. Significant differences between treatment and vehicle are represented as: *P < 0.05; ‡P < 0.01; †P < 0.001.