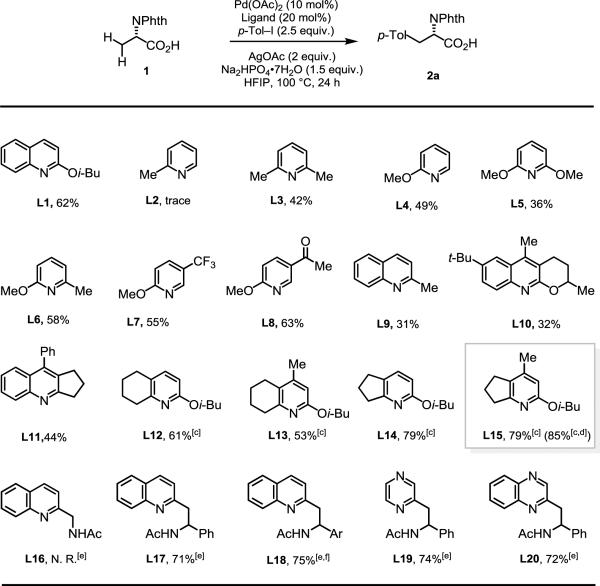
Table 1.
Experiments were performed with substrate 1 (0.1 mmol), Pd(OAc)2 (10 mol%), AgOAc (0.2 mmol), Ar–I (0.25 mmol), Na2HPO4·7H2O (0.15 mmol), Ligand (20 mol%), HFIP (1.0 mL), 100 °C, 24 h.
Determined by 1H NMR analysis ofthe crude product using CH2Br2 as an internal standard.
[c] HFIP (2.0 mL).
[d] L15 (10 mol%)+L8 (10 mol%).
[e] Conditions: substrate (0.1 mmol), Pd(OAc)2 (10 mol%), Ag2CO3 (0.2 mmol), Ar–I (0.25 mmol), ligand (10 mol%), K2HPO4 (0.1 mmol), HFIP (1.0 mL), 100 °C, 24 h.
[f] Ar = 3,5-di-t-butylphenyl