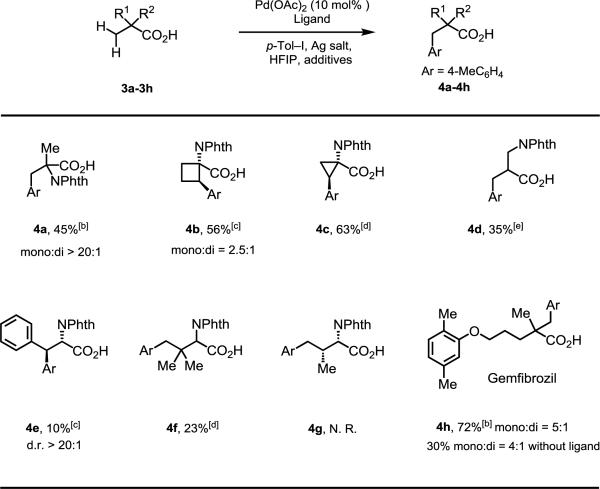
Table 3.
Arylation of Other Amino Acids and Carboxylic Acids.[a]
Isolated yields are shown based on corresponding methyl ester.
[b] Conditions: substrate (0.1 mmol), Pd(OAc)2 (10 mol %), AgOAc (0.2 mmol), Ar–I (0.25 mmol), Na2HPO4·7H2O (0.15 mmol), L15 (20 mol%), HFIP (1.0 mL), 100 °C, 24 h.
[c] Conditions: substrate (0.1 mmol), Pd(OAc)2 (10 mol%), AgOAc (0.2 mmol), Ar–I (0.25 mmol), Na2HPO4·7H2O (0.15 mmol), L18 (12 mol%), HFIP (1.0 mL), 100 °C, 24 h.
[d] Conditions: substrate (0.1 mmol), Pd(OAc)2 (10 mol%), Ag2CO3 (0.2 mmol), Ar–I (0.25 mmol), L18 (12 mol%), K2HPO4 (0.1 mmol), HFIP (1.0 mL), 100 °C, 24 h.
[e] Conditions: substrate (0.1 mmol), Pd(OAc)2 (10 mol%), AgOAc (0.2 mmol), Ar–I (0.25 mmol), Na2HPO4·7H2O (0.15 mmol), L8 (20 mol%), HFIP (1.0 mL), 100 °C, 24 h.