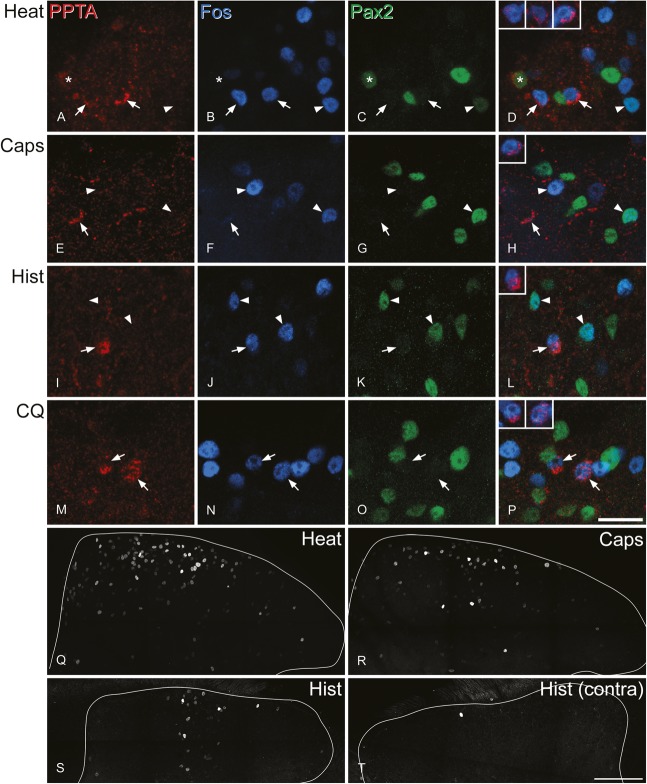
Figure 5.
Fos immunoreactivity after noxious or pruritic stimulation. (A–D, E–H, I–L, and M–P) are from mice that were stimulated with noxious heat, capsaicin, histamine, or chloroquine, respectively. In each case, the same field from superficial dorsal horn is shown stained for preprotachykinin A (PPTA) (red), Fos (blue), and Pax2 (green), together with a merged image. The insets in (D, H, L, and P) show staining for PPTA (red) and NeuN (blue) in the marked PPTA-immunoreactive cells. (A–D) The noxious stimulus resulted in numerous Fos+ neurons. This field contains 2 PPTA-immunoreactive/Pax2-negative cells that have Fos-immunoreactive nuclei (arrows). In addition, a PPTA-negative cell that is positive for both Pax2 and Fos is shown with an arrowhead, and a PPTA-positive/Pax2-positive cell that lacks Fos is indicated with an asterisk. (E–H) Relatively few of the PPTA+ excitatory (Pax2-negative) cells showed Fos after capsaicin injection. This field shows one of these cells that lacks Fos (arrow). Two Fos-immunoreactive cells are indicated with arrowheads. The one on the left is negative for Pax2 while that on the right is Pax2+. (I–L) This field from a histamine-injected mouse shows a PPTA+ excitatory (Pax2-negative) cell that contains Fos (arrow). In addition, 2 PPTA-negative cells that are immunoreactive for both Fos and Pax2 are indicated (arrowheads). (M–P) After stimulation with chloroquine, several Fos-immunoreactive neurons are visible, and 2 of these (marked with arrows) are PPTA-immunoreactive excitatory (Pax2-negative) neurons. Images are projections of 3 (E–H), 5 (A–D), or 4 (I–P) optical sections at 1 μm z-spacing. (Q–S) Show lower magnification views of the ipsilateral dorsal horn from mice treated with noxious heat, capsaicin, or histamine (the same sections as those in A–L) scanned to reveal Fos. (T) Shows the contralateral side of the histamine-treated animal. Scale bars: A-P = 20 μm; Q-T = 100 μm.