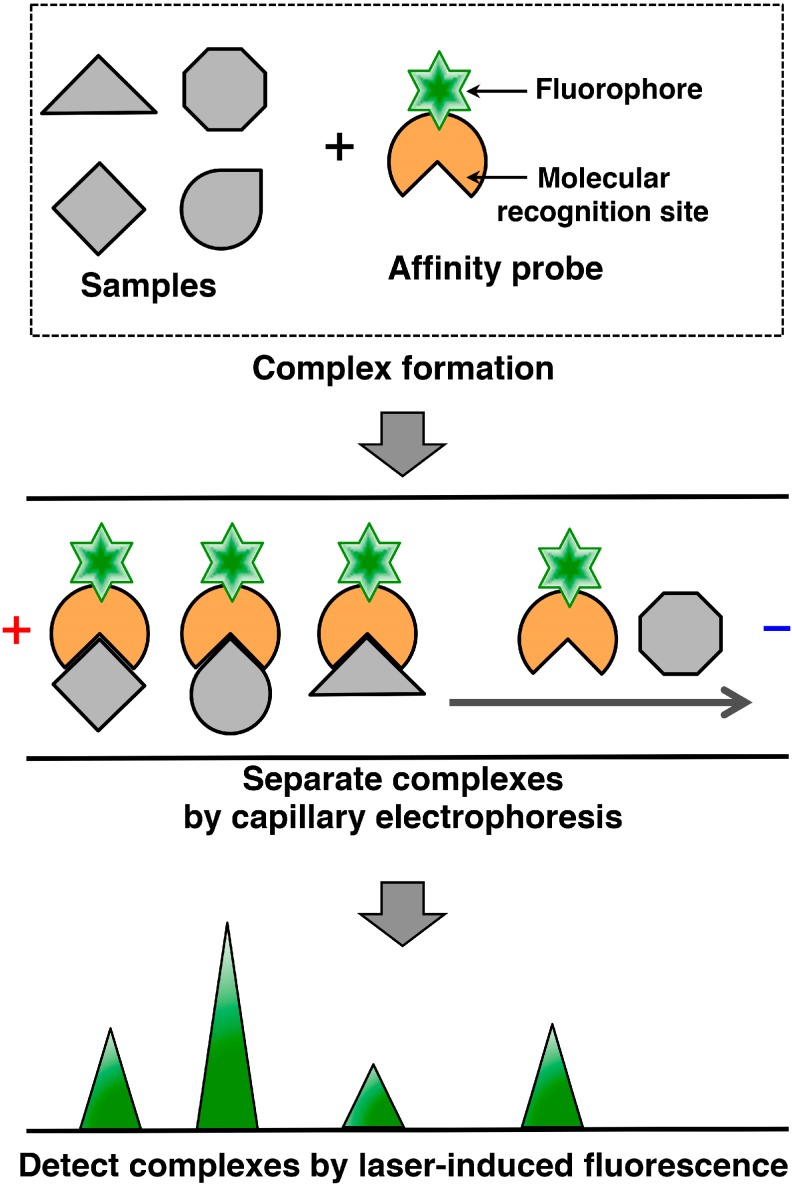
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of capillary affinity electrophoresis (CAE). Fluorescently-labeled affinity probes are mixed with the sample, and the resultant complexes are separated by capillary electrophoresis. The principle of separation is the change in mobility resulting from the difference in the dynamic equilibrium between the target molecules and the affinity probes in the electrophoretic field. This method also permits the electrical migration of only those molecules that are strongly bound to the affinity probes.