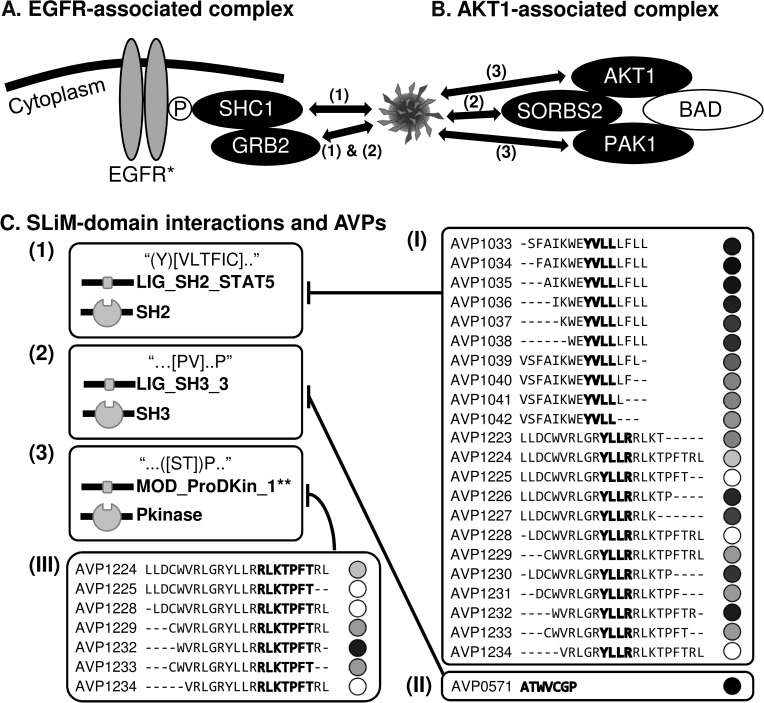
Fig 5. Case examples.
(A) The EGFR-associated complex (S5 Table, Complex ID: 176). (B) The AKT1-associated complex (S5 Table, Complex ID: 180). (C) Types of SLiM-domain interactions (indicated by (1), (2), and (3)) that mediate the targeting of protein complexes, and three sets of AVPs (indicated by (I), (II) and (III)) containing the corresponding SLiM that exhibits inhibition activity (indicated by bar-headed arrows) are shown. Proteins represented by black ovals are VIPsdirect; by gray ovals are VIPsindirect; and by white ovals are not VIPs (i.e. not in the virus-host PPI network). Double-headed arrows in panel A and B indicate predicted HCV-host PPIs in our analysis. Viral SLiM(s) are highlighted within the amino acid sequence of the AVP and are accompanied by its relative efficacy (in shaded circles) in inhibiting HCV entry (see the vertical bar for the normalized inhibition score in Fig 4 on the right of its top panel). The regular expression of each SLiM sequence as annotated in the ELM database [11] is shown within quotation marks in the SLiM-domain interactions (1), (2), and (3). *EGFR is a known HCV entry factor. **MOD_ProDKin_1 is representative of the MOD_family SLiMs (see Fig 3).