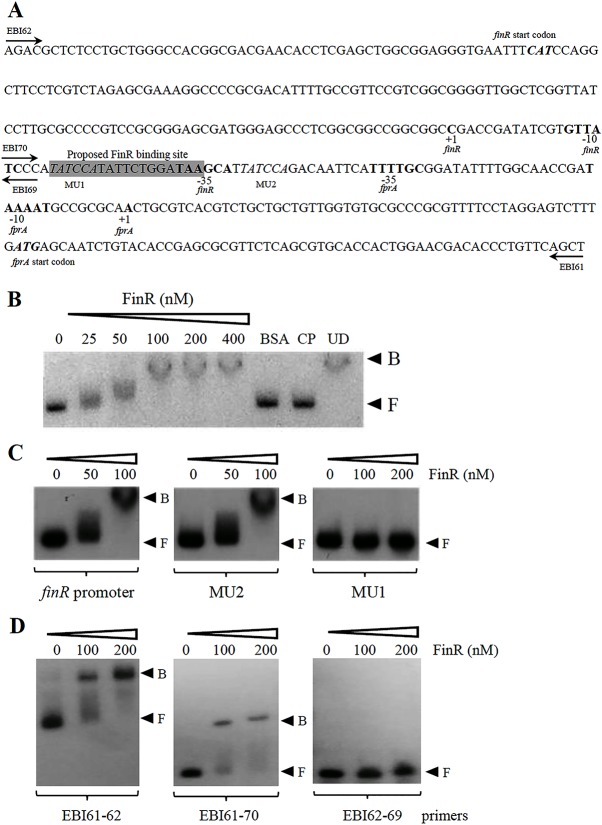
Fig 4. Characterization and binding of purified FinR to the finR-fprA promoter.
(A) Nucleotide sequence showing the finR-fprA promoter structure. +1 indicates the transcriptional start site, and the bold sequences are the putative -35 and -10 promoter motifs. CAT and ATG are the translational start codons of FinR and FprA, respectively. The box shaded gray represents the proposed FinR binding site. (B), (C), and (D) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay using purified FinR. A 32P –labeled DNA fragment (B), mutagenized MU1 and MU2 fragments (C), or the promoter fragments (EBI61-62), with (EBI 61–70) and without (EBI 62–69) proposed FinR binding site (D) spanning the finR-fprA promoter was incubated with increasing amounts of FinR. BSA represents an unrelated protein (2.5 μg BSA). CP and UD signify the cold probe (100 ng unlabeled promoter fragment) and unrelated DNA (1 μg of pUC18 plasmid), respectively, that were added to the binding reaction mixture containing 100 nM FinR. F and B indicate free and bound probes, respectively.