Extended Data Figure 2.
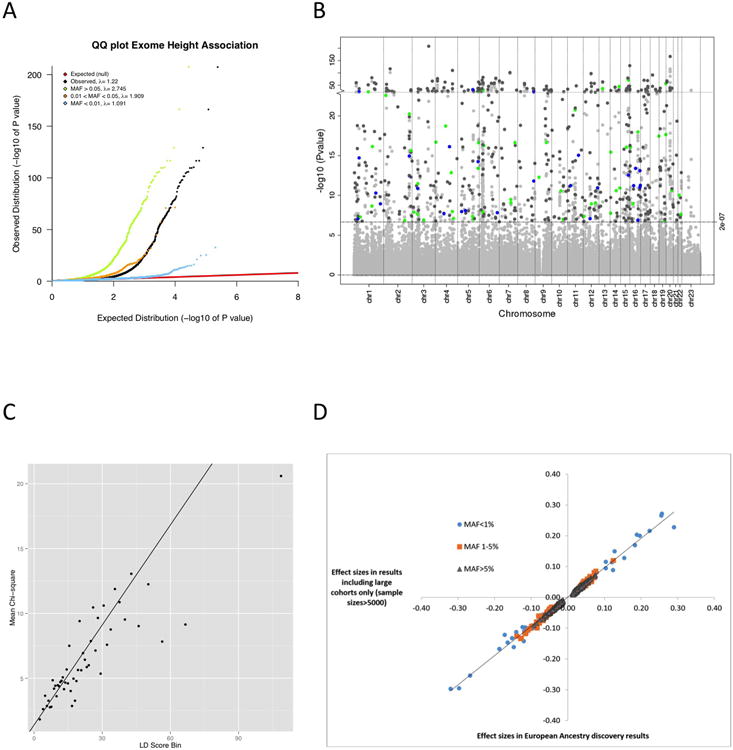
Height ExomeChip association results. (A) Quantile-quantile plot of ExomeChip variants and their association to adult height under an additive genetic model in individuals of European ancestry. We stratified results based on allele frequency. (B) Manhattan plot of all ExomeChip variants and their association to adult height under an additive genetic model in individuals of European ancestry with a focus on the 553 independent SNPs, of which 469 have MAF>5% (grey), 55 have MAF between 1 and 5% (green), and 29 have MAF<1% (blue). (C) Linkage disequilibrium (LD) score regression analysis for the height association results in European-ancestry studies. In the plot, each point represents an LD Score quantile, where the x-axis of the point is the mean LD Score of variants in that quantile and the y-axis is the mean χ2 statistic of variants in that quantile. The LD Score regression slope of the black line is calculated based on Equation 1 in Bulik-Sullivan et al.30 which is estimated upwards due to the small number of common variants (N=15,848) and the design of the ExomeChip. The LD score regression intercept is 1.4, the λGC is 2.7, the mean χ2 is 7.0, and the ratio statistic of (intercept -1) / (mean χ2 -1) is 0.067 (standard error=0.012). (D) Scatter plot comparison of the effect sizes for all variants that reached significance in the European-ancestry discovery results (N=381,625) and results including only studies with sample sizes >5000 individuals (N=241,453).
