Fig. 3. Revealing interaction types.
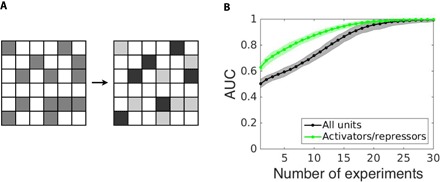
(A) Beyond distinguishing existing from missing interactions (schematically represented by the medium gray and white adjacency matrix), activating and inhibiting interactions may be separately detected (dark gray, light gray, and white matrix). (B) The reconstruction quality (AUC) benefits from the separate reconstruction of different types of interactions (green curve) compared to joint reconstruction of existing and missing interactions (gray curve), and increases with the number of driving-response experiments. Data are shown for random networks of N = 50 Goodwin oscillators with a regular incoming degree of 4 and a number of sampled time points of 100; shading indicates SD across ensembles of network realizations.
