Figure 3. Signaling pathway analysis of Mnk inhibition.
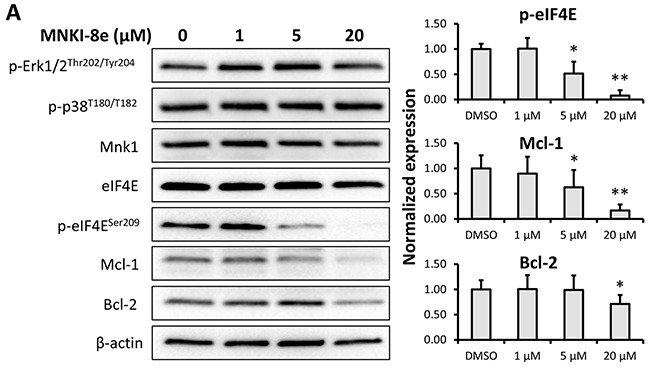
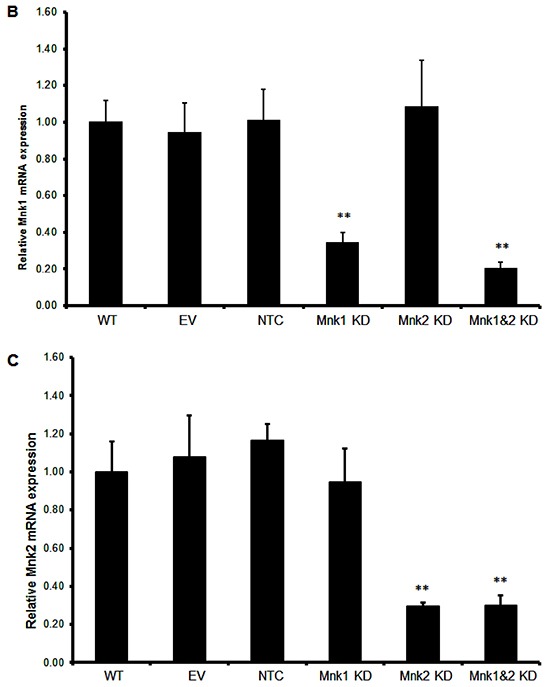
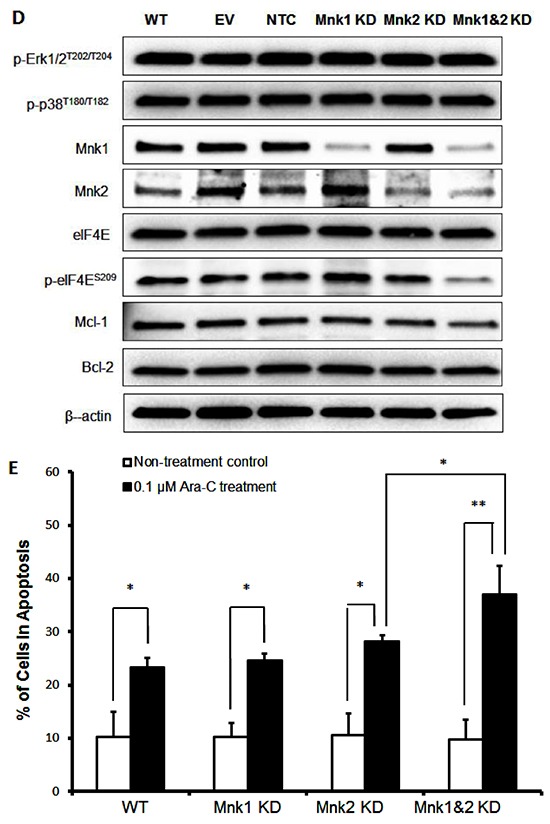
A. MV4-11 cells were exposed to MNKI-8e for 24 h at the concentrations shown and analyzed by Western blotting for the phosphorylation of Erk1/2, p-38 and eIF4E. The expression of anti-apoptotic proteins Mcl-1 and Bcl-2 were also analyzed. β-Actin was used as an internal control. B. and C. Lentiviral vectors with Mnk1 or Mnk2 shRNA were used to transfect and knockdown mRNA of Mnk1 (i.e. Mnk1 KD), Mnk2 (Mnk2 KD) and double knockdown Mnk1&2 (i.e. Mnk1&2 KD) in MV4-11 cells. The respective KD levels were confirmed by RT-qPCR when compared to non-transfected MV4-11 cells (WT), the cells treated with empty vector (EV) and non-target control shRNA vector (NTC). Vertical bars represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Data was analyzed by the Student's t-test **p ≤ 0.01. D. The effects of Mnk1 KD, Mnk2 KD and Mnk1&2 KD on the MAP kinases and Mnk-eIF4E in MV4-11 cells by Western blot analysis compared to cells treated with EV and NTC. β-Actin was used as an internal control. E. Ara-C induction of apoptosis in Mnk1 KD, Mnk2 KD and Mnk1&2 KD cells. The cells were exposed to 0.1 μM Ara-C for 24 h and apoptosis was determined using annexin V/PI assay where annexin V+/PI- plus annexin V/PI+ cells were shown. Data were analyzed by the Student's t-test *p ≤ 0.05 or **p ≤ 0.01. DMSO diluent was used as control in each experiment.
